Product Description
Human Prostate Acid Phosphatase is also known as human prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP, ACP) is an alternative marker to Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) for prostate malignancy. Prostatic Acid phosphatase (PAP) is a phosphatase, a type of enzyme, used to free attached phosphate groups from other molecules during digestion. Acid Phosphatase is stored in lysosomes and functions when these fuse with endosomes, which are acidified while they function; therefore, Human Acid Phosphatase has an acid pH optimum below 7.0.
Biovision | P1445 | Prostatic Acid Phosphatase, Human Semen DataSheet
Biomolecule/Target :
Synonyms: ACP, PAP, Acid Phos, 5'-nucleotidase, 5'-NT, Ecto-5'-nucleotidase, Thiamine monophosphatase, TMPase, PAPf39
Alternates names: ACP, PAP, Acid Phos, 5'-nucleotidase, 5'-NT, Ecto-5'-nucleotidase, Thiamine monophosphatase, TMPase, PAPf39
Taglines: Marker for the progression of prostate cancer
NCBI Gene ID #: 55
NCBI Gene Symbol: ACPP
Gene Source: Human
Accession #: P15309
Recombinant: False
Source: Human Semen
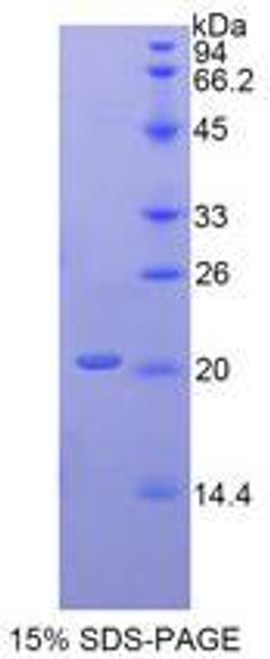
Purity by SDS-PAGE: >98%
Assay: SDS-PAGE.
Purity:
Assay #2:
Endotoxin Level:
Activity (Specifications/test method):
Biological activity: > 100 U/mg (Dimension® Clinical Chemistry System)
Results:
Binding Capacity:
Unit Definition: One unit will catalyze the hydrolysis of one micromole of thymolphthalein monophosphate to thymolphthalein and phosphate per minute at pH 5.6 and 37°C.
Molecular Weight: ~100,000
Concentration:
Appearance: Lyophilized powder
Physical form description: Lyophilized
Reconstitution Instructions: Reconstitute in water to the concentration of 10 mg/mL
Amino acid sequence:
Handling: Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Usage:
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL