Product Description
XAB2 Polyclonal Antibody | E-AB-53550 | Elabscience
Type: Polyclonal Antibody
Synonyms: 0610041O14Rik, adapter protein ATH 55, Adapter protein ATH-55, Ath55, AV025587, Crn related protein kim1 , crn-related protein kim1, DKFZp762C1015, HCNP, HCNP protein, HCRN, KIAA1177, NTC90, PP3898, Pre-mRNA-splicing factor SYF1, Protein HCNP, RNA splicing factor, SYF1, SYF1 homolog, SYF1 homolog, RNA splicing factor , SYF1 pre mRNA splicing factor, SYF1, Xab2, XPA binding protein 2, XPA-binding protein 2
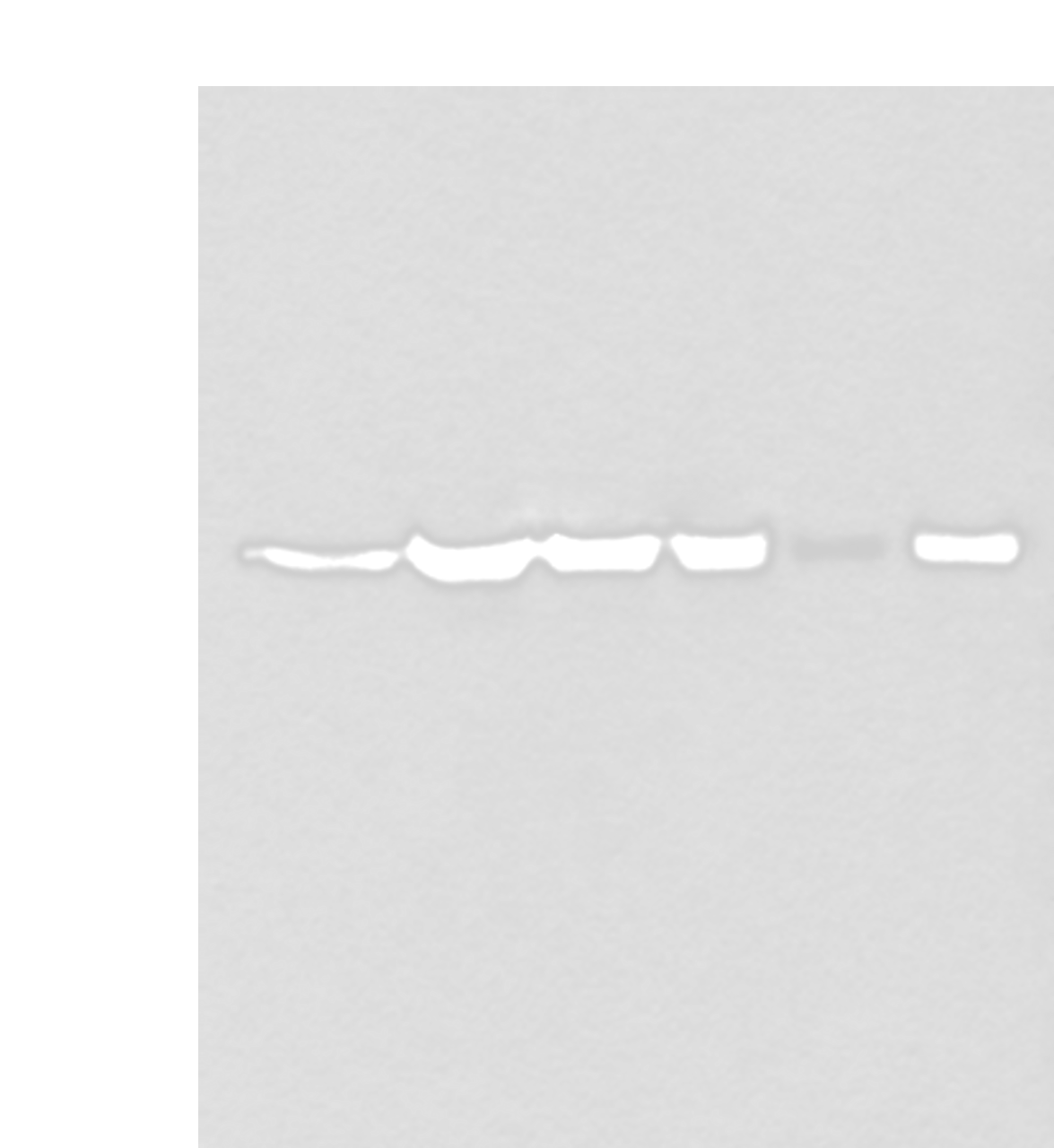
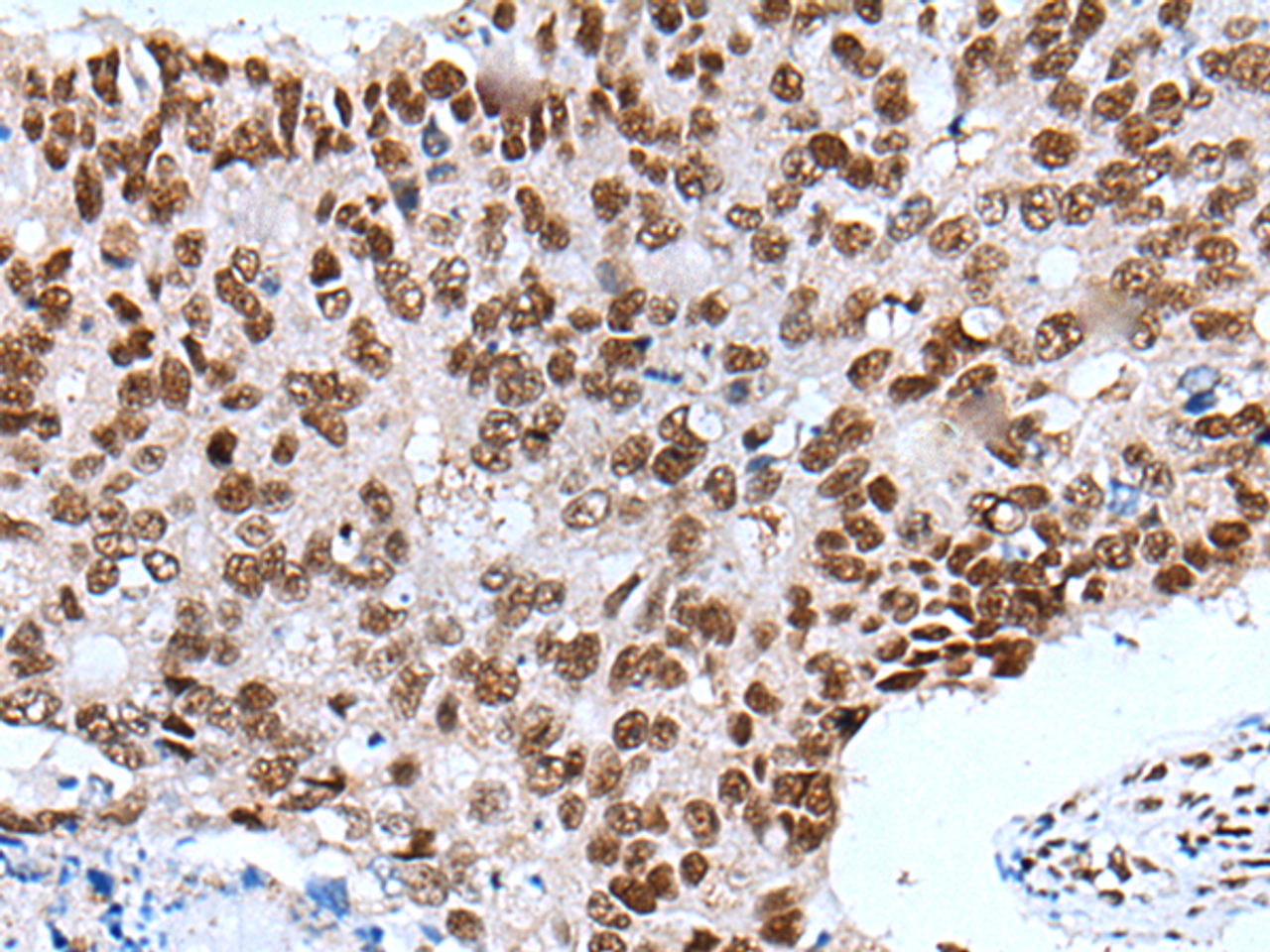
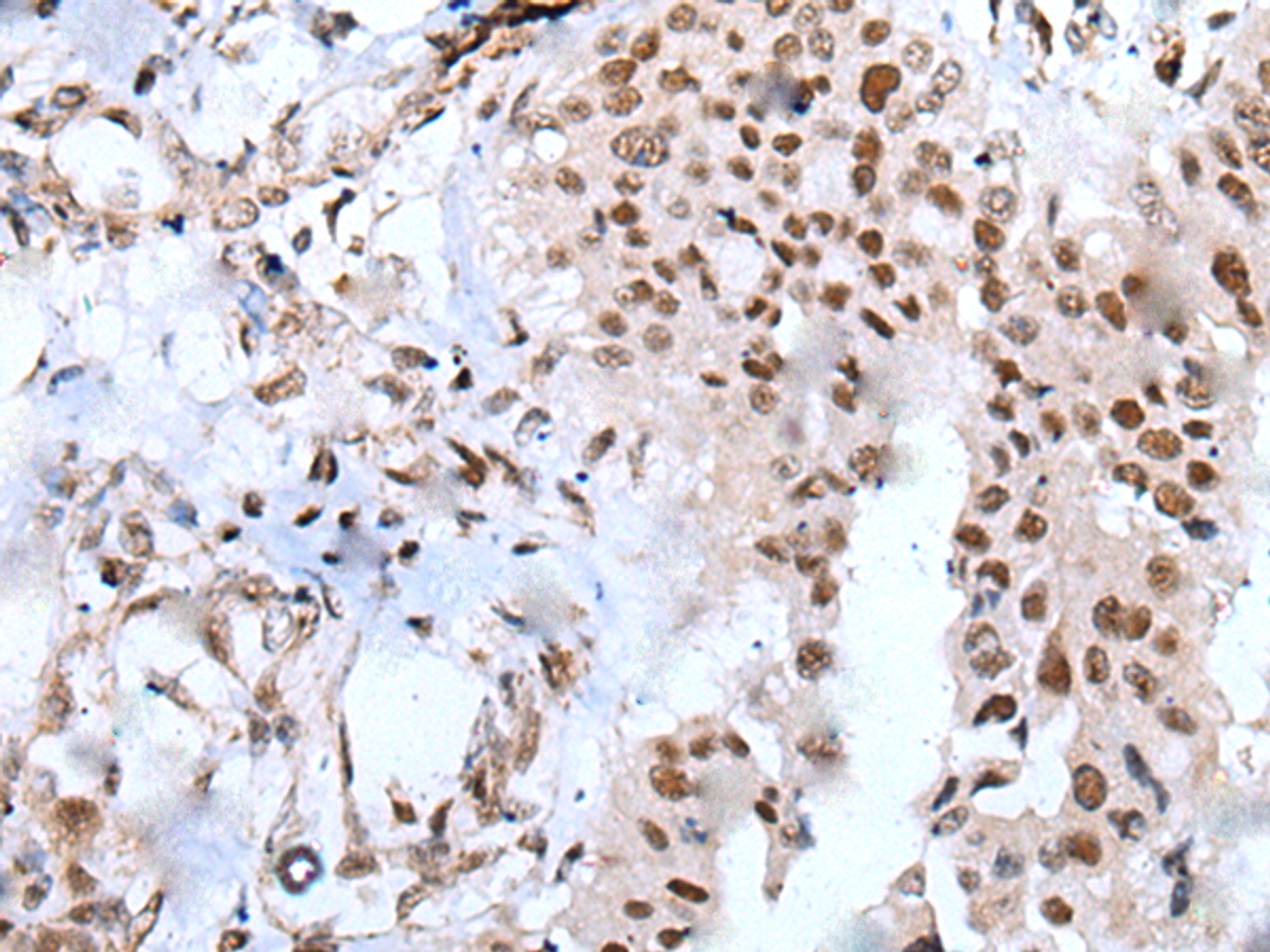
Application: WB, IHC, ELISA
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Host: Rabbit
Isotype: IgG
Reserch Areas: Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Background: HCNP, also known as XAB2 (Xeroderma pigmentosum group A (XPA) binding protein 2), HCRN, SYF1 or NTC90, is a nuclear protein that participates in transcription, transcription-coupled repair (TCR) and pre-mRNA splicing. It contains fifteen tetratricopeptide repeat motifs and associates with nucleotide excision repair machinery. More specifically, HCNP associates with Cockayne syndrome group A and B proteins (CSA and CSB), RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) and XPA in response to DNA damage and is believed to function in the TCR pathway. HCNP also functions as an essential component of a pre-mRNA splicing complex of the spliceosome (composed of AQR (aquarius), PRP19, CCDC16, HCNP, ISY1 and Cyclophilin E) and is required for proper RNA synthesis in the cell. In addition, HCNP functions as a component of the RAR corepressor complex with RAR and HDAC3 and exhibits an inhibitory effect on ATRA-induced cell differentiation. This suggests that HCNP may function as useful target in cancer therapy.
Concentration: 0.4 mg/mL
Storage: Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide of human XAB2
Buffer: PBS with 0.05% NaN3 and 40% Glycerol, pH7.4
Purification Method: Antigen affinity purification
Dilution: WB 1:500-1:2000, IHC 1:25-1:100, ELISA 1:5000-1:10000
Clone: N/A
Conjugation: Unconjugated
Molecular Weight(Calculated): 100 kDa
Molecular Weight(Observed): Refer to figures
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL