Product Description
The EpiQuik™ 8-OhG RNA Damage Quantification Direct Kit (Colorimetric) is a complete set of optimized buffers and reagents for directly detecting oxidative RNA damage (8-OhG) status using RNA isolated from any species such as mammals, plants, fungi, bacteria, and viruses in a variety of forms including, but not limited to, cultured cells, fresh and frozen tissues, paraffin-embedded tissues, and body fluid samples. The kit has the following advantages and features:
- Colorimetric assay with easy-to-follow steps for convenience and speed. The entire procedure can be completed within 3 hours.
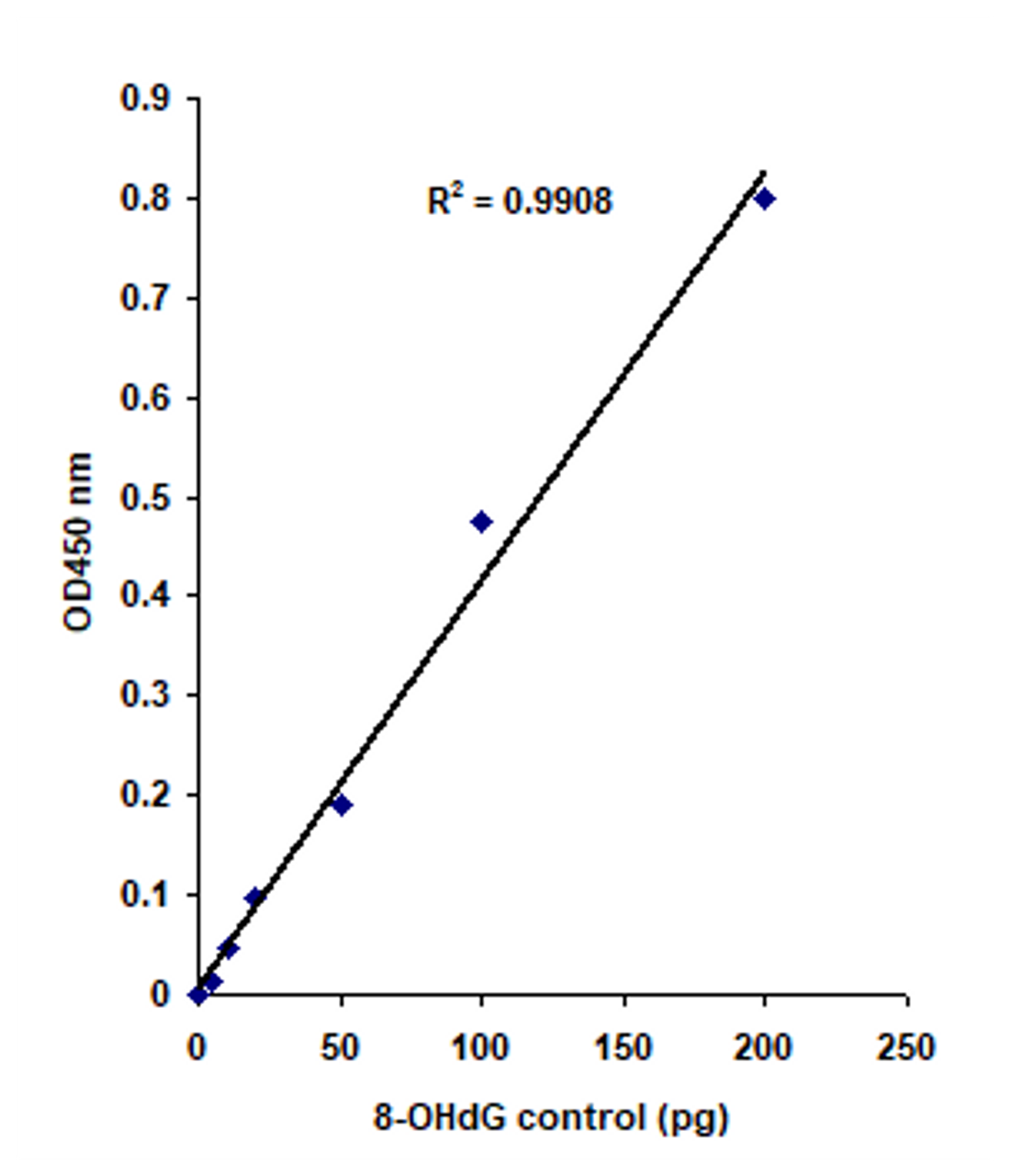
- High sensitivity, of which the detection limit can be as low as 2 pg of 8-OhG.
- High specificity by detecting only 8-OhG within the indicated concentration range of the sample RNA.
- Direct detection of 8-OhG using intact RNA, which eliminates interference from high molecular weight compounds, such as carbohydrates and proteins that are often seen in competitive 8-OhG assays.
- Highly convenient assay with direct use of RNA isolated from cells or tissues, no need for RNA digestion or hydrolysis.
- Universal positive and negative controls are included, which are suitable for quantifying 8-OhG from any species.
- Strip-well microplate format makes the assay flexible for manual or high throughput analysis.
- Simple, reliable, and consistent assay conditions.
Background Information
8-hydroxyguanosine (8-OhG or 8-oxoG) is an oxidized derivative of guanosine and is generated by hydroxyl radicals, singlet oxygen, and one-electron oxidants in cellular RNA. As a modified nucleoside base, 8-OhG is considered important not only because of its abundance but also because of its mutagenic mispairing that occurs during RNA synthesis and may induce errors in gene expression. 8-OhG also participates in epigenetic regulation of gene activation/repression by affecting chromatin modification. Unlike oxidative DNA that is quickly repaired by base excision repair pathways intracellularly, oxidized RNA can remain in the cell for hours after a short insult of oxidative stress, and these oxidative marks on RNA could be identified as an early indicator of cell death. Evidence shows that increased levels of 8-OhG are closely correlated with exposure to harmful environmental factors such as ionizing radiation, industrial chemicals, air pollution, cigarette smoking, and cancer chemotherapy. It has also been demonstrated that increased concentrations of 8-OhG are pathogenically linked to a variety of age-associated diseases, including cancer, coronary heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Compared with the urine 8-OhG assay that mainly reflects the balance between oxidative damage and the repair rate of the whole body, directly quantifying the 8-OhG content in different cells/tissues in normal and disease states would allow tissue-specific oxidative damage of RNA to be identified. Therefore, more useful information for better understanding oxidative damage-disease relationships, which benefits diagnostics and therapeutics of the disease, can be obtained.
Principle & Procedure
This kit contains all reagents necessary for the quantification of Oxidative RNA damage (8-OhG). In this assay, RNA is bound to strip wells that are specifically treated to have a high RNA affinity. 8-OhG is detected using capture and detection antibodies. The detected signal is enhanced and then quantified colorimetrically by reading the absorbance in a microplate spectrophotometer. The amount of 8-OhG is proportional to the OD intensity measured.
Starting Materials & Input Amount
The input material required is RNA, which can be isolated from various tissue or cell samples such as cells from flask or microplate cultured cells, fresh and frozen tissues, paraffin-embedded tissues, blood, body fluid samples, etc. The amount of RNA for each assay can be 100 ng to 300 ng. For optimal quantification, the input RNA amount should be 300 ng, as basal 8-OhG is generally less than 0.01% of total RNA.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL