Product Description
ATP1A2 Antibody | 15-211 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-70 of human ATP1A2 (NP_000693.1) .
Research Area: Cancer, Signal Transduction
Tested Application: WB
Application: WB: 1:500 - 1:2000
Specificiy: N/A
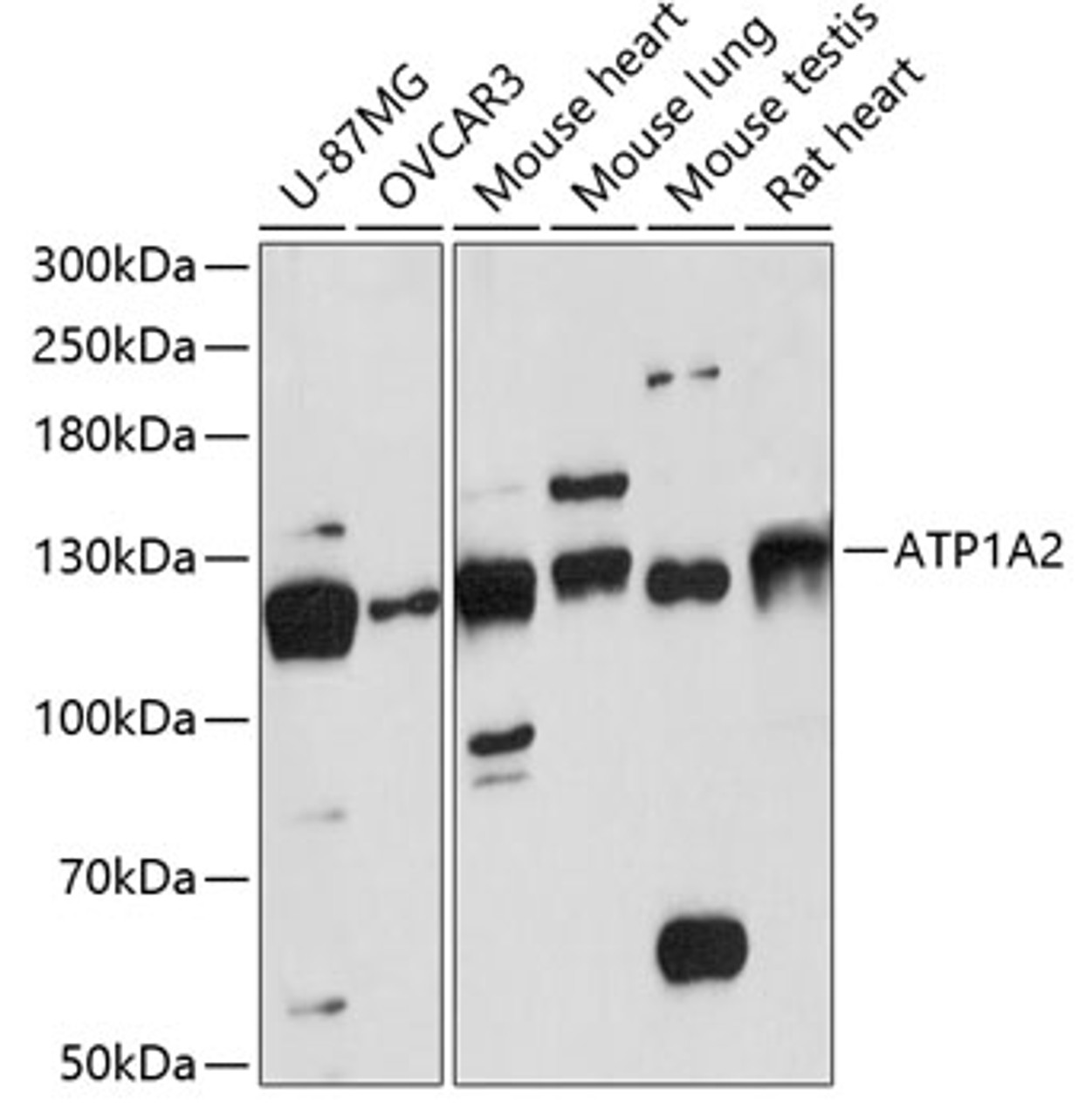
Positive Control 1: U-87MG
Positive Control 2: OVCAR3
Positive Control 3: Mouse heart
Positive Control 4: Mouse lung
Positive Control 5: Mouse testis
Positive Control 6: Rat heart
Molecular Weight: Observed: 112kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Affinity purification
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: Store at -20˚C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: FHM2, MHP2, sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-2, ATPase Na+/K+ transporting alpha 2 polypeptide, Na (+) /K (+) ATPase alpha-2 subunit, Na+/K+ ATPase, alpha-A (+) catalytic polypeptide, Na+/K+ ATPase, alpha-B polypeptide, sodium pump subunit alpha-2, sodium-potassium ATPase catalytic subunit alpha-2, sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase alpha-2 chain
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+ -ATPases. Na+/K+ -ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta) . The catalytic subunit of Na+/K+ -ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes an alpha 2 subunit. Mutations in this gene result in familial basilar or hemiplegic migraines, and in a rare syndrome known as alternating hemiplegia of childhood.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL