Product Description
F13A1 Antibody | 15-630 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 600-732 of human F13A1 (NP_000120.2) .
Research Area: Other
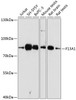
Tested Application: WB
Application: WB: 1:500 - 1:2000
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Jurkat
Positive Control 2: SH-SY5Y
Positive Control 3: BxPC-3
Positive Control 4: Mouse testis
Positive Control 5: Rat brain
Positive Control 6: Rat testis
Molecular Weight: Observed: 83kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Affinity purification
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: Store at -20˚C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: F13A1, coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide, RP11-232H4.1, F13A, Coagulation factor XIII A chain, Coagulation factor XIII, A polypeptide, TGase, bA525O21.1 (coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide) , coagulation factor XIII A1 subunit, factor XIIIa
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: This gene encodes the coagulation factor XIII A subunit. Coagulation factor XIII is the last zymogen to become activated in the blood coagulation cascade. Plasma factor XIII is a heterotetramer composed of 2 A subunits and 2 B subunits. The A subunits have catalytic function, and the B subunits do not have enzymatic activity and may serve as plasma carrier molecules. Platelet factor XIII is comprised only of 2 A subunits, which are identical to those of plasma origin. Upon cleavage of the activation peptide by thrombin and in the presence of calcium ion, the plasma factor XIII dissociates its B subunits and yields the same active enzyme, factor XIIIa, as platelet factor XIII. This enzyme acts as a transglutaminase to catalyze the formation of gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine crosslinking between fibrin molecules, thus stabilizing the fibrin clot. It also crosslinks alpha-2-plasmin inhibitor, or fibronectin, to the alpha chains of fibrin. Factor XIII deficiency is classified into two categories: type I deficiency, characterized by the lack of both the A and B subunits; and type II deficiency, characterized by the lack of the A subunit alone. These defects can result in a lifelong bleeding tendency, defective wound healing, and habitual abortion.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL