Product Description
ARMER Antibody | 3305 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: ARMER antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to 15 amino acids near the C-terminus of human ARMER.
The immunogen is located within the last 50 amino acids of ARMER.
Research Area: Apoptosis
Tested Application: E, WB, IHC-P, IF
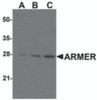
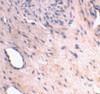
Application: ARMER antibody can be used for detection of ARMER by Western blot at 0.5 to 2 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 2 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in mouse samples; Immunohistochemistry in human samples and Immunofluorescence in mouse samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1408 - Mouse Small Intestine Tissue Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: ARMER Antibody is Ion exchange chromatography purified.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: ARMER Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: ARMER antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: ARMER Antibody: AIP1, ARMER, SPG61, ARL6IP, KIAA0069, ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 6-interacting protein 1, ARL-6-interacting protein 1
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: ARMER Antibody: Apoptosis is important for normal development and tissue homeostasis. It is mediated by various caspases and ultimately results in the activation of endogenous endonucleases that degrade cellular DNA. Although apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is thought to be mediated by caspase-12, other caspases such as caspase-9 are also thought to be activated following ER stress. Recently, ARMER, a novel integral ER-membrane protein was shown to protect cells from ER stress-induced apoptosis. Analysis of the caspase proteolytic cascade suggests that ARMER acts by inhibiting caspase-9 activity, although the mechanism for this remains unkown. It should be noted that ARMER is not related to the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAP) family and does not contain any baculoviral IAP repeat (BIR) domains.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL