Product Description
SOX4 Antibody | 8123 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: SOX4 antibody was raised against a 16 amino acid peptide near the amino terminus of human SOX4.
The immunogen is located within the first 50 amino acids of SOX4.
Research Area: Stem Cell, Apoptosis
Tested Application: E, WB, IHC-P, IF
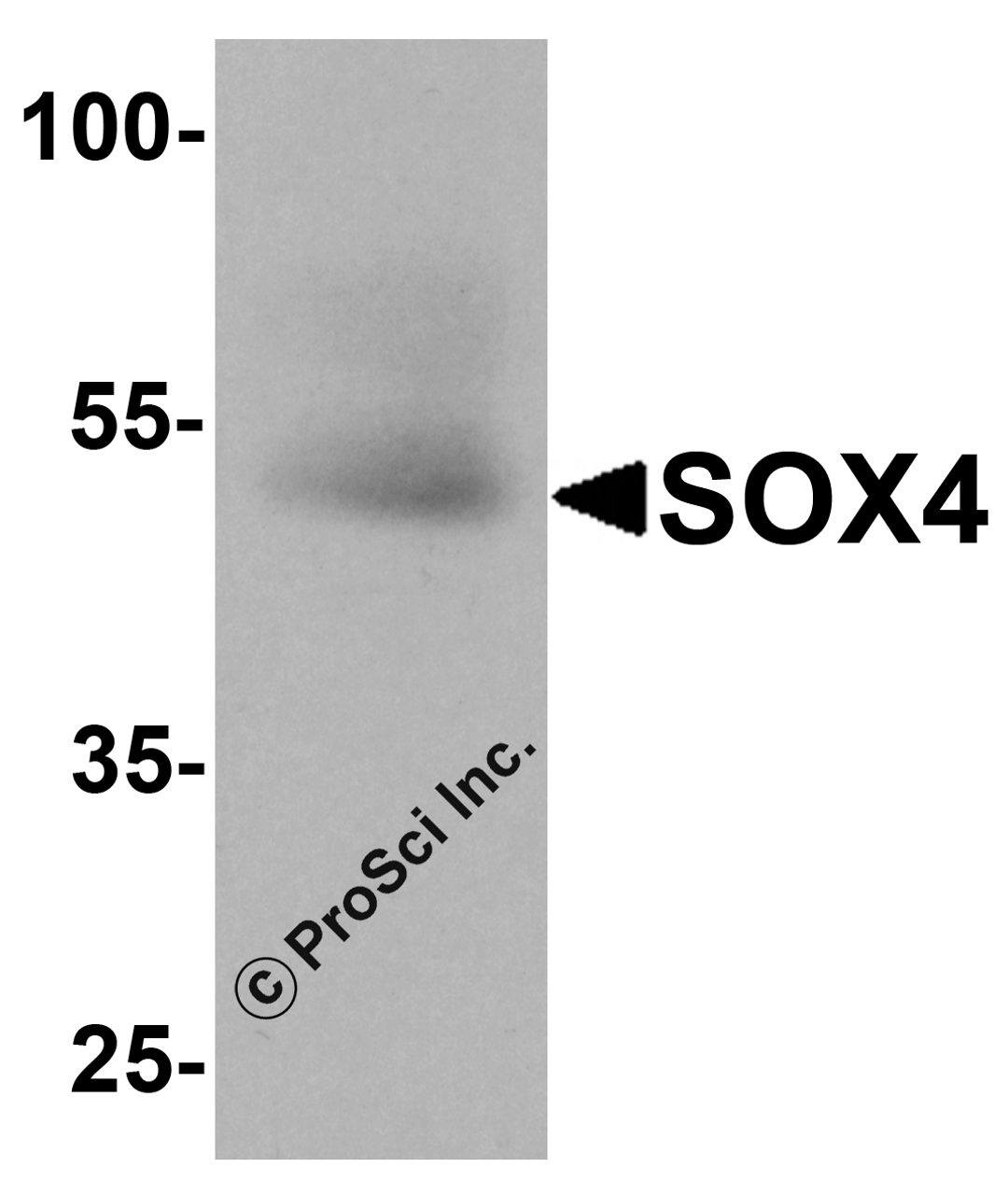
Application: SOX4 antibody can be used for detection of SOX4 by Western blot at 1 - 2 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples; Immunohistochemistry in rat samples and Immunofluorescence in rat samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: SOX4 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive.
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1313 - Human Testis Tissue Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Predicted: 52 kDa
Observed: 520 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: SOX4 antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: SOX4 antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: SOX4 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year.
Alternate Name: SRY (Sex determining region Y) -box 4, Transcription factor SOX-4, EVI16
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: SOX4 is a member of the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) family of transcription factors involved in the regulation of embryonic development and in the determination of the cell fate (1, 2) . It may act as a transcriptional regulator after forming a protein complex with other proteins, such as syndecan binding protein (syntenin) (3) . SOX4 contains one HMG box DNA-binding domain and may function in the apoptosis pathway leading to cell death. It has also been suggested to play a role in tumorigenesis and may mediate downstream effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH) and PTH-related protein (PTHrP) in bone development (4, 5) .
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL