Product Description
SPAM1 Antibody | 18-516 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 100-300 of human SPAM1 (NP_003108.2) .
Research Area: Cancer, Cell Cycle, Signal Transduction
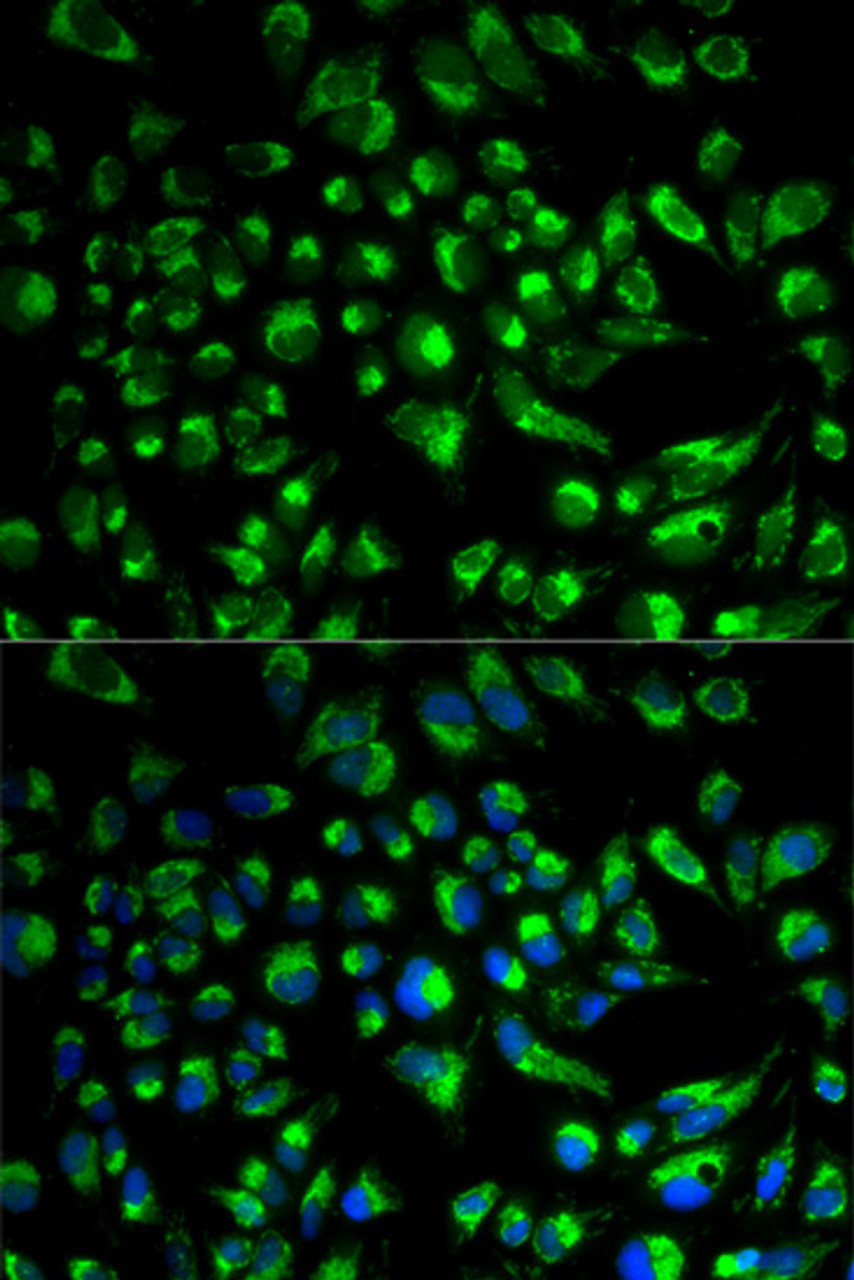
Tested Application: WB, IF
Application: WB: 1:500 - 1:2000
IF: 1:50 - 1:200
Specificiy: N/A
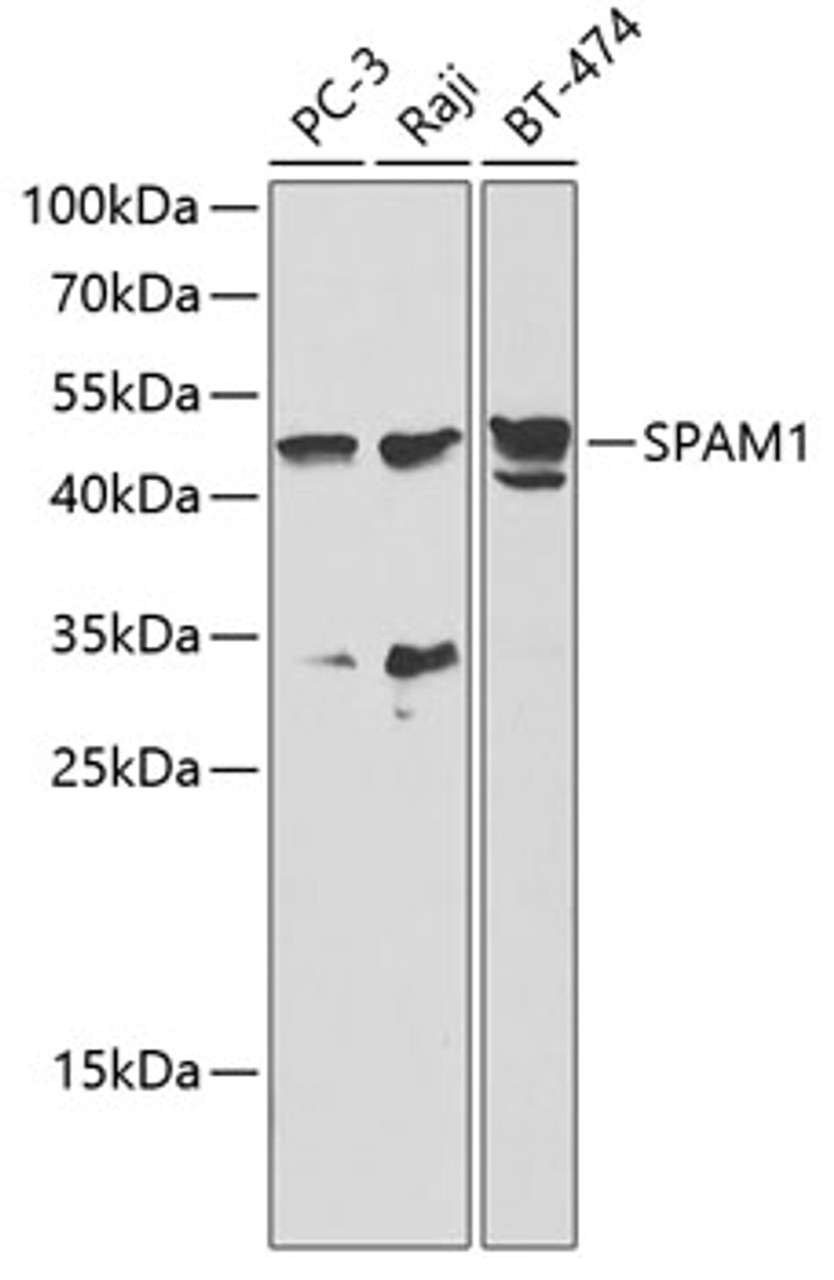
Positive Control 1: PC-3
Positive Control 2: Raji
Positive Control 3: BT-474
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Observed: 47kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Affinity purification
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: Store at -20˚C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: HEL-S-96n, HYA1, HYAL1, HYAL3, HYAL5, PH-2PH2SPAG15, hyaluronidase PH-2PH-20 hyaluronidase, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein Li 96n, hyal-PH2hyaluronoglucosaminidase PH-2sperm adhesion molecule 1 (PH-20 hyaluronidase, zona pellucida binding) , sperm surface protein PH-20
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: Hyaluronidase degrades hyaluronic acid, a major structural proteoglycan found in extracellular matrices and basement membranes. Six members of the hyaluronidase family are clustered into two tightly linked groups on chromosome 3p21.3 and 7q31.3. This gene was previously referred to as HYAL1 and HYA1 and has since been assigned the official symbol SPAM1; another family member on chromosome 3p21.3 has been assigned HYAL1. This gene encodes a GPI-anchored enzyme located on the human sperm surface and inner acrosomal membrane. This multifunctional protein is a hyaluronidase that enables sperm to penetrate through the hyaluronic acid-rich cumulus cell layer surrounding the oocyte, a receptor that plays a role in hyaluronic acid induced cell signaling, and a receptor that is involved in sperm-zona pellucida adhesion. Abnormal expression of this gene in tumors has implicated this protein in degradation of basement membranes leading to tumor invasion and metastasis. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL