Product Description
CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy5) | 98-832 | ProSci
Host: Hamster
Reactivity: Mouse
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Mouse dendritic epidermal cell line Y245
Research Area: Immunology
Tested Application: IHC-Fr, Flow
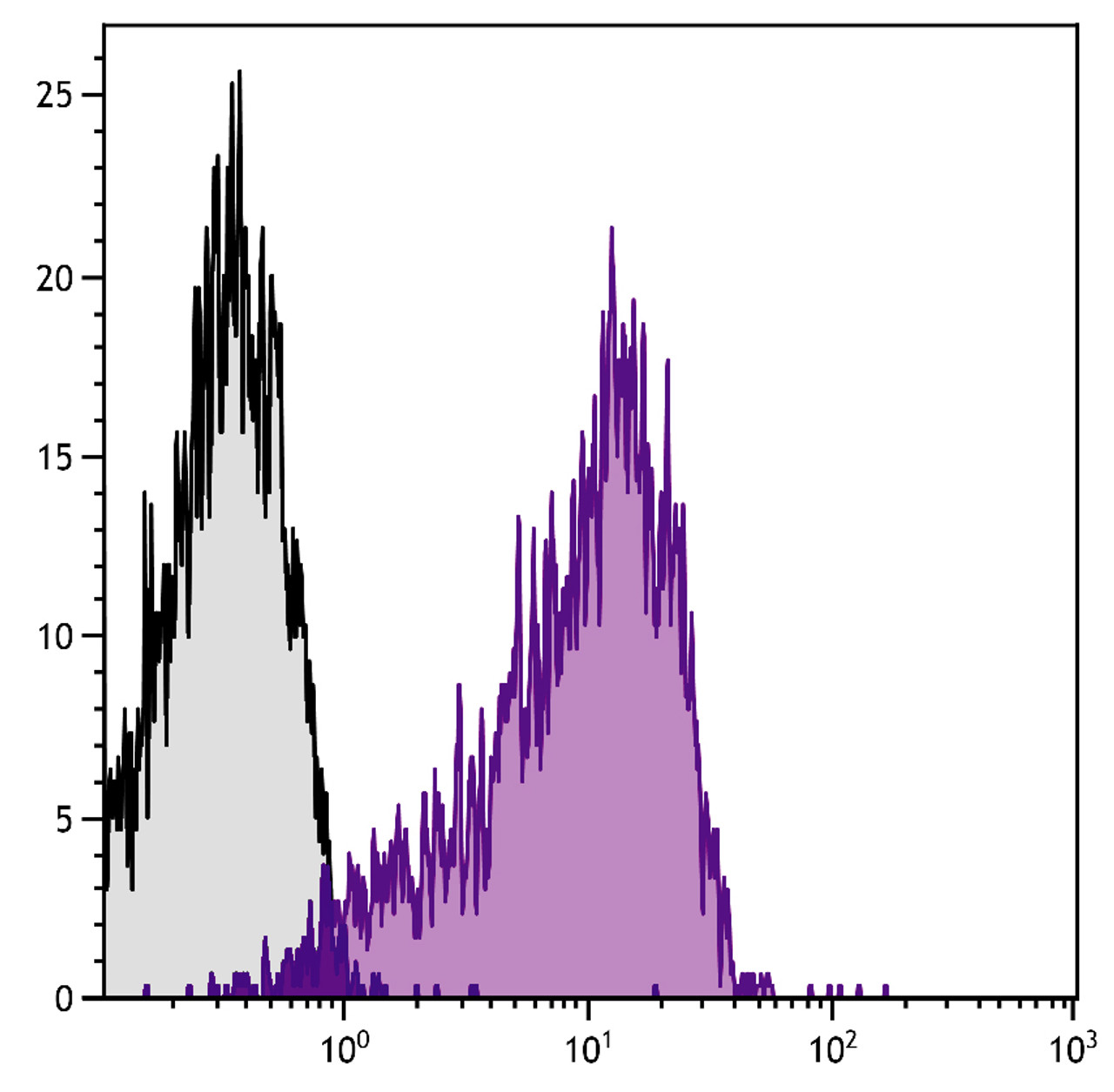
Application: CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] for use in flow cytometry assays.
Specificiy: CD69
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: N/A
Clonality: Monoclonal
Clone: [H1.2F3]
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: PE-Cy5
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: Supplied in PBS/NaN3 and a stabilizing agent
Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: Store vial at 2-8˚C
Alternate Name: VEA, very early activation antigen, AIM, EA1, MLR3, gp34/28, Leu-23
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: CD69, also known as very early activation (VEA) antigen, is a disulfide-linked transmembrane homodimer whose differentially glycosylated subunits range from 35-39 kDa. It is a C-type lectin most closely related to the NKR-P1 and Ly-49 NK cell-activation molecules. CD69 is widely expressed on hematopoietic cells, including lymphocytes, neutrophils and eosinophils. Although not detectable on resting lymphocytes, its expression is rapidly upregulated upon activation of T, B and NK cells, and neutrophils. Constitutive expression of CD69 on subsets of thymocytes suggests that it may be involved in regulation of developmental events in addition to its role in activation of a variety of hematopoietic cells. The monoclonal antibody H1.2F3 augments PMA-induced T-cell proliferation and induces redirected lysis of Fc receptor-bearing target cells by NK cells.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL

![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy5) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy5)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/1280x1280/products/576131/813737/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__50142.1649092132.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy5) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy5)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/100x100/products/576131/813737/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__50142.1649092132.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy5) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy5)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/576131/813737/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__50142.1649092132.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/576129/813733/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__60777.1649092131.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy7) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE-Cy7)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/576132/813739/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__02592.1649092132.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/576571/814426/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__32553.1649092224.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/576574/814431/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__36744.1649092225.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (APC) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (APC)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/576130/813735/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__21677.1649092131.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (Biotin) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (Biotin)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/576573/814429/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__21251.1649092225.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (FITC) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (FITC)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/576572/814427/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__22973.1649092225.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/556025/765042/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__76998.1649086712.png?c=2)
![CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE) CD69 Antibody [H1.2F3] (PE)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/556024/765041/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__11206.1649086712.png?c=2)