Product Description
SIRT7 Antibody | 5775 | ProSci
Host: Chicken
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Bovine: (100%)
Immunogen: SIRT7 antibody was raised against a 19 amino acid synthetic peptide near the amino terminus of human SIRT7.
The immunogen is located within amino acids 50 - 100 of SIRT7.
Research Area: Homeostasis
Tested Application: E, WB
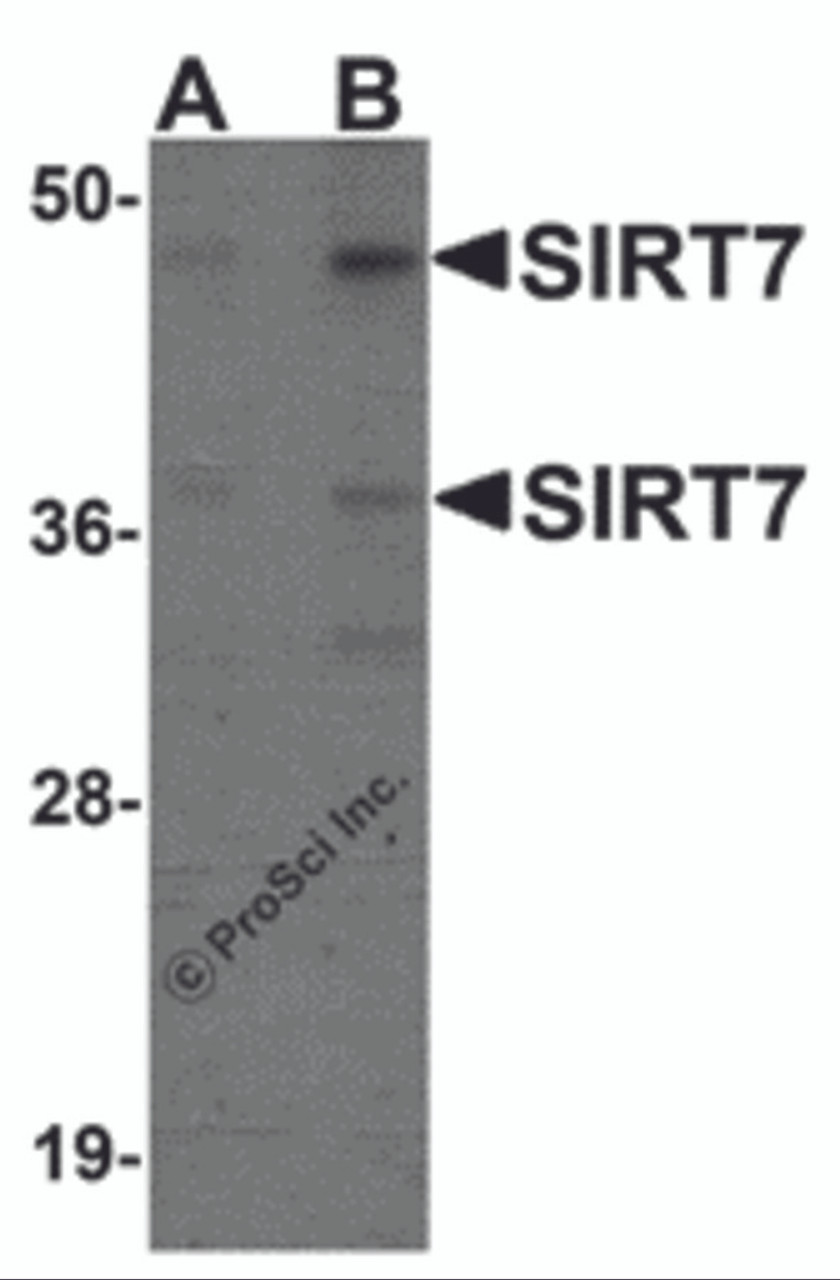
Application: SIRT7 antibody can be used for detection of SIRT7 by Western blot at 0.5 - 1 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1210 - HEK293 Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: SIRT7 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgY
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: SIRT7 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: SIRT7 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: SIRT7 Antibody: SIR2L7, SIR2L7, NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-7, Regulatory protein SIR2 homolog 7
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: SIRT7 Antibody: The Silent Information Regulator (SIR2) family of genes are highly conserved from prokaryotes to eukaryotes and have important functions in the regulation of metabolism, growth and differentiation, inflammation, cellular survival, as well as in senescence and lifespan extension. Sirtuins, including SIRT1-7, are human homologs of yeast Sir2p. Sirtuins are NAD+-dependent histone/protein deacetylases (HDAC) which regulate cellular metabolism, e.g. energy metabolism, and thereby are associated with aging and several age-related diseases. SIRT7 is a nucleolar protein that positively regulates RNA polymerase I transcription and has been postulated to enable cells to sustain critical functions by inhibiting cell growth under severe stress conditions.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL