Product Description
HIG1 Antibody | 6489 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Mouse: (79%) , Rat: (74%)
Immunogen: HIG1 antibody was raised against a 19 amino acid synthetic peptide near the amino terminus of human HIG1.
The immunogen is located within the first 50 amino acids of HIG1.
Research Area: Cancer, Cell Cycle
Tested Application: E, WB, ICC, IF
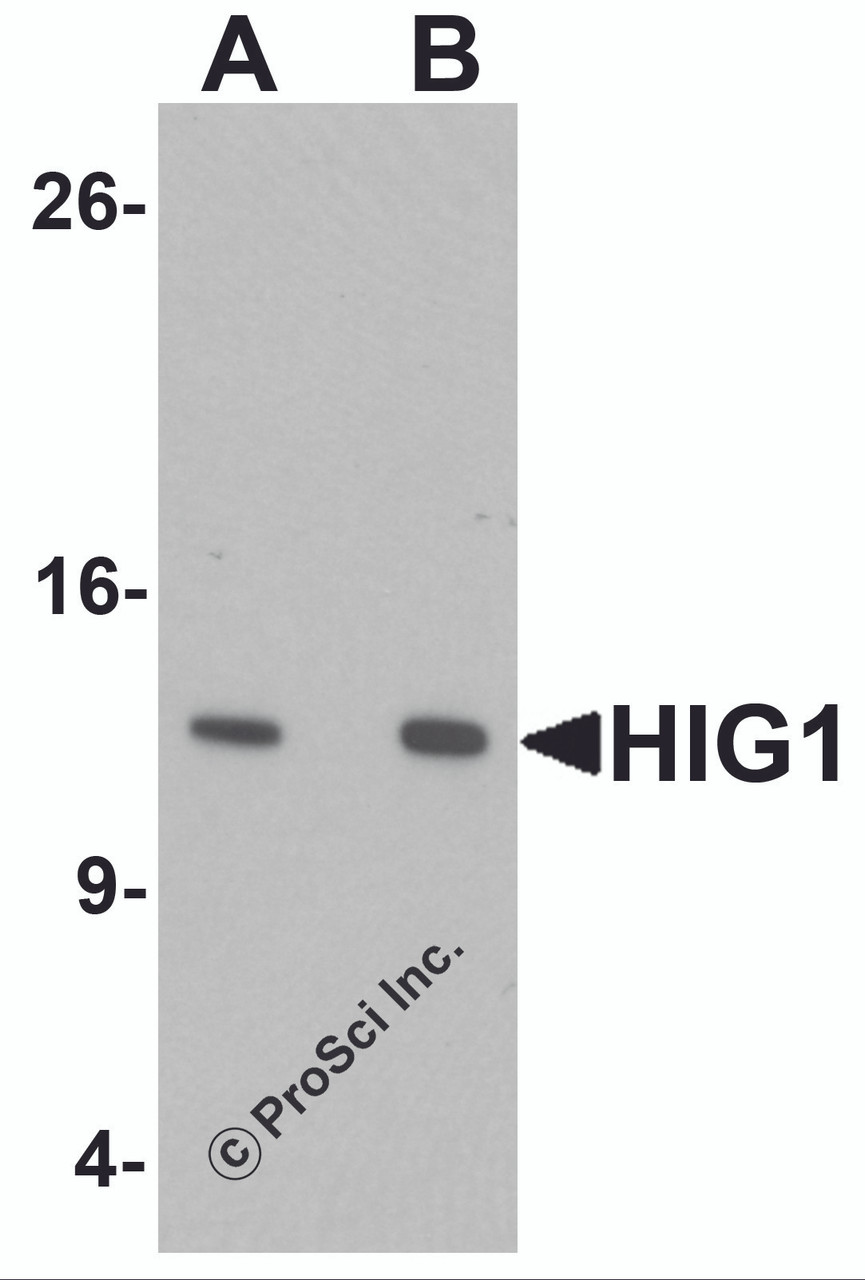
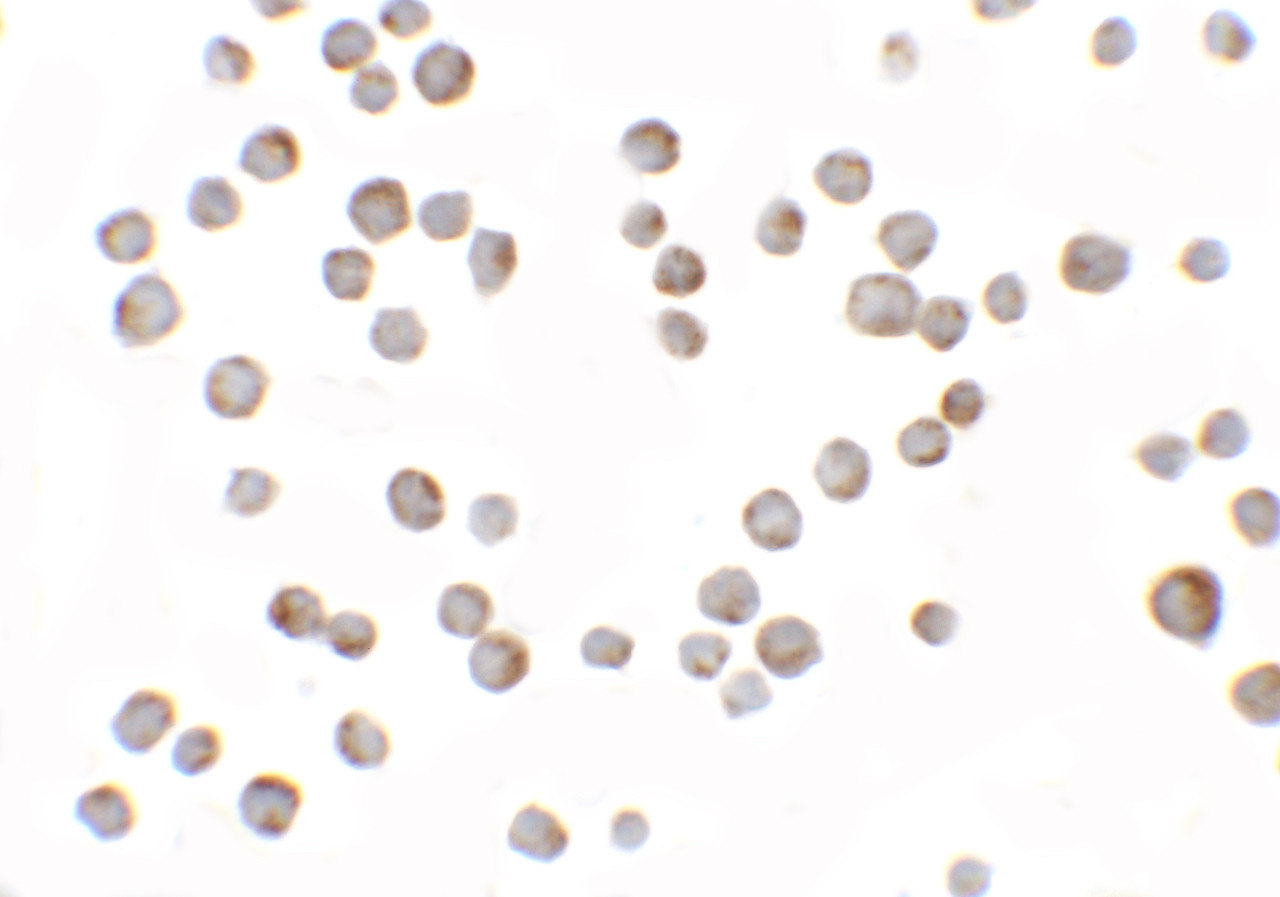
Application: HIG1 antibody can be used for detection of HIG1 by Western blot at 0.5 - 1 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunocytochemistry starting at 2.5 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 10 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples; Immunocytochemistry in human samples and Immunofluorescence in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: HIG1 antibody is predicted to not cross-react with HIG2
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1210 - HEK293 Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: Cat. No. 17-010 - HEK293 Cell Slide
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: HIG1 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: HIG1 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: HIG1 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: HIG1 Antibody: HIG1, RCF1a, HIG1, HSPC010, HIG1 domain family member 1A, mitochondrial, Hypoxia-inducible gene 1 protein
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: HIG1 Antibody: HIG1 and HIG2 (Hypoxia-inducible gene 1 and 2, respectively) are known to be induced by hypoxic conditions. HIG1 is induced by hypoxia and by glucose deprivation in cultured cells. In addition, tumor xenografts derived from human cervical cancer cells display increased expression of HIG1 and HIG2 when they are deprived of oxygen. Unlike HIG2, which is ubiquitously expressed and might be an activator and target of the canonical Wnt pathway, the function and the mechanisms underlying its regulation of HIG1 still remained unknown. The putative link between hypoxia and an oncogenic signaling pathway might play an important role in tumorigenesis.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL