Product Description
HSPA5 Antibody | 57-011 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: This HSPA5 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a recombinant protein encoding full length human HSPA5.
Research Area: Other
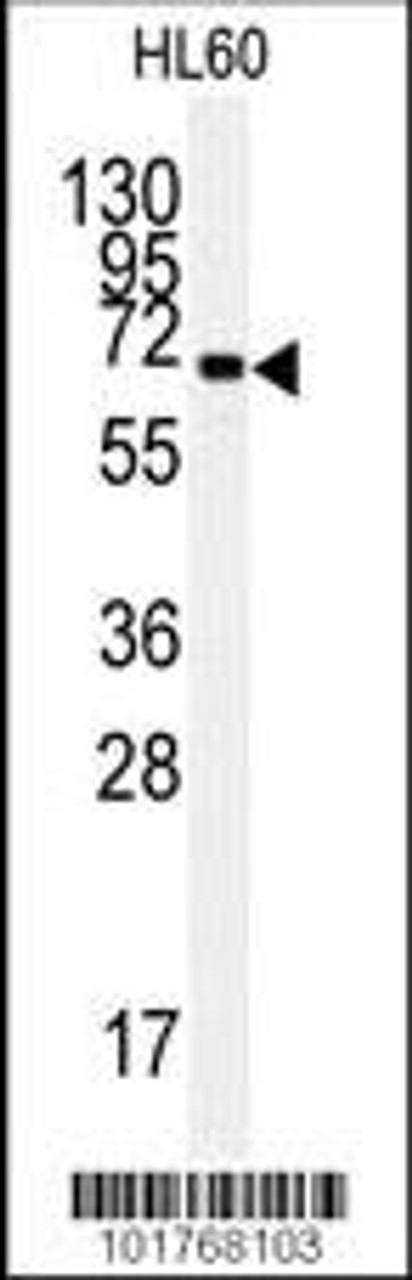
Tested Application: WB, IHC-P, IF, Flow
Application: For WB starting dilution is: 1:1000
For IHC-P starting dilution is: 1:50~100
For IF starting dilution is: 1:10~50
For FACS starting dilution is: 1:10~50
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: 72 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: Rabbit Ig
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: Supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide.
Concentration: batch dependent
Storage Condition: Store at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein, GRP-78, Endoplasmic reticulum lumenal Ca (2+) -binding protein grp78, Heat shock 70 kDa protein 5, Immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein, BiP, HSPA5, GRP78
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: In cooperation with other chaperones, HSP70s stabilize preexistent proteins against aggregation and mediate the folding of newly translated polypeptides in the cytosol as well as within organelles. The HSP70s in mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum play an additional role by providing a driving force for protein translocation. They are involved in signal transduction pathways in cooperation with HSP90. They participate in all these processes through their ability to recognize nonnative conformations of other proteins. They bind extended peptide segments with a net hydrophobic character exposed by polypeptides during translation and membrane translocation, or following stress-induced damage.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL












![HSPA5 Antibody [AMM22210G] HSPA5 Antibody [AMM22210G]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/870571/1162638/logo__92149.1659788186__82934.1659866704.png?c=2)

![HSPA5 Antibody [APR31107G] HSPA5 Antibody [APR31107G]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/871352/1163419/logo__92149.1659788186__60012.1659868028.png?c=2)
