Product Description
MAGEA4 Antibody | 8191 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: MAGEA4 antibody was raised against a 16 amino acid peptide near the amino terminus of human MAGEA4.
The immunogen is located within the first 50 amino acids of MAGEA4.
Research Area: Stem Cell, Cancer
Tested Application: E, WB, IHC-P, IF
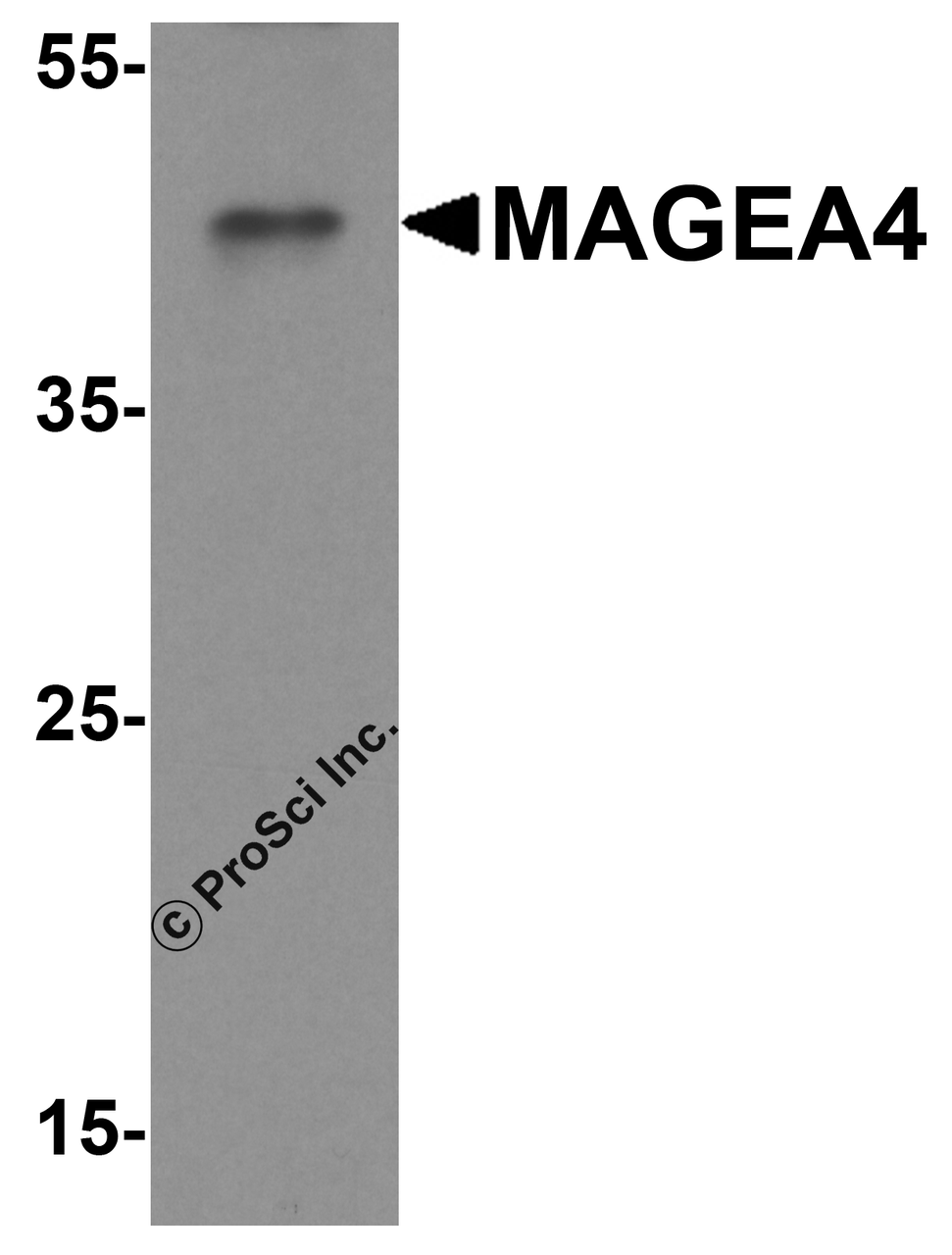
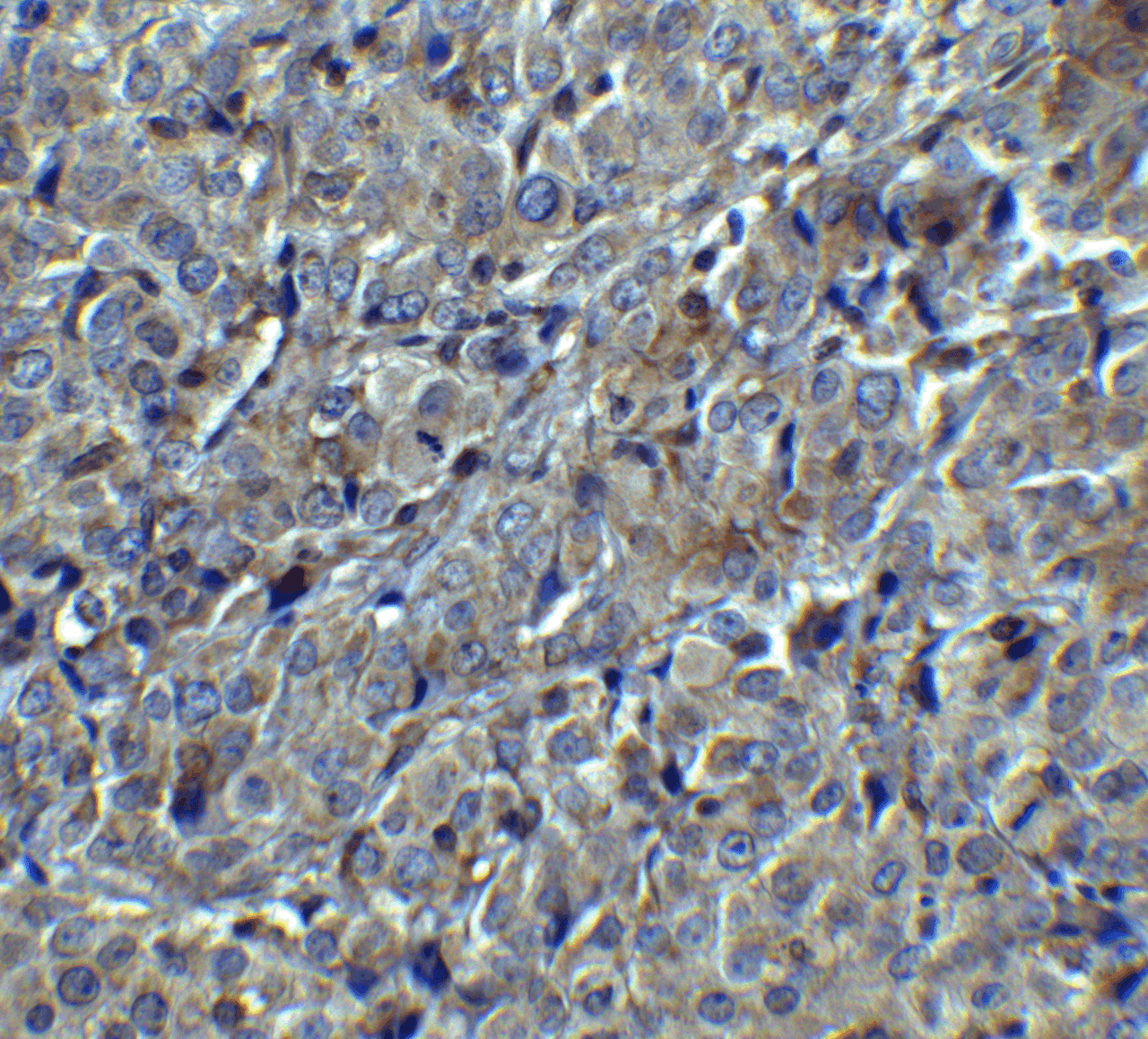
Application: MAGEA4 antibody can be used for detection of MAGEA4 by Western blot at 1 - 2 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples; Immunohistochemistry in human samples; Immunocytochemistry in human samples and Immunofluorescence in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: MAGEA4 antibody is human specific. At least four isoforms of MAGEA4 are known to exist.
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1202 - A431 Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: Cat. No. 10-001 - Human Breast Tissue Slide
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Predicted: 35 kDa
Observed: 45 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: MAGEA4 antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: MAGEA4 antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: MAGEA4 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year.
Alternate Name: Melanoma antigen family A4, MAGE4, MAGE-41, MAGE4A, MAGE-4 antigen, MAGE4B, MAGE-X2, MAGE-X2 antigen, Melanoma-associated antigen 4
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: MAGEA4 is a member of the melanoma-associated antigen family that consists of a number of antigens recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (1) . MAGEA4 may serve as a target for antitumoral vaccination and may play a role in embryonal development and tumor transformation or aspects of tumor progression. It is expressed in many tumors of several types, such as melanoma, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, lung carcinoma and breast carcinoma and have been implicated in some hereditary disorders, such as dyskeratosis congenital (2-4) .
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL