Product Description
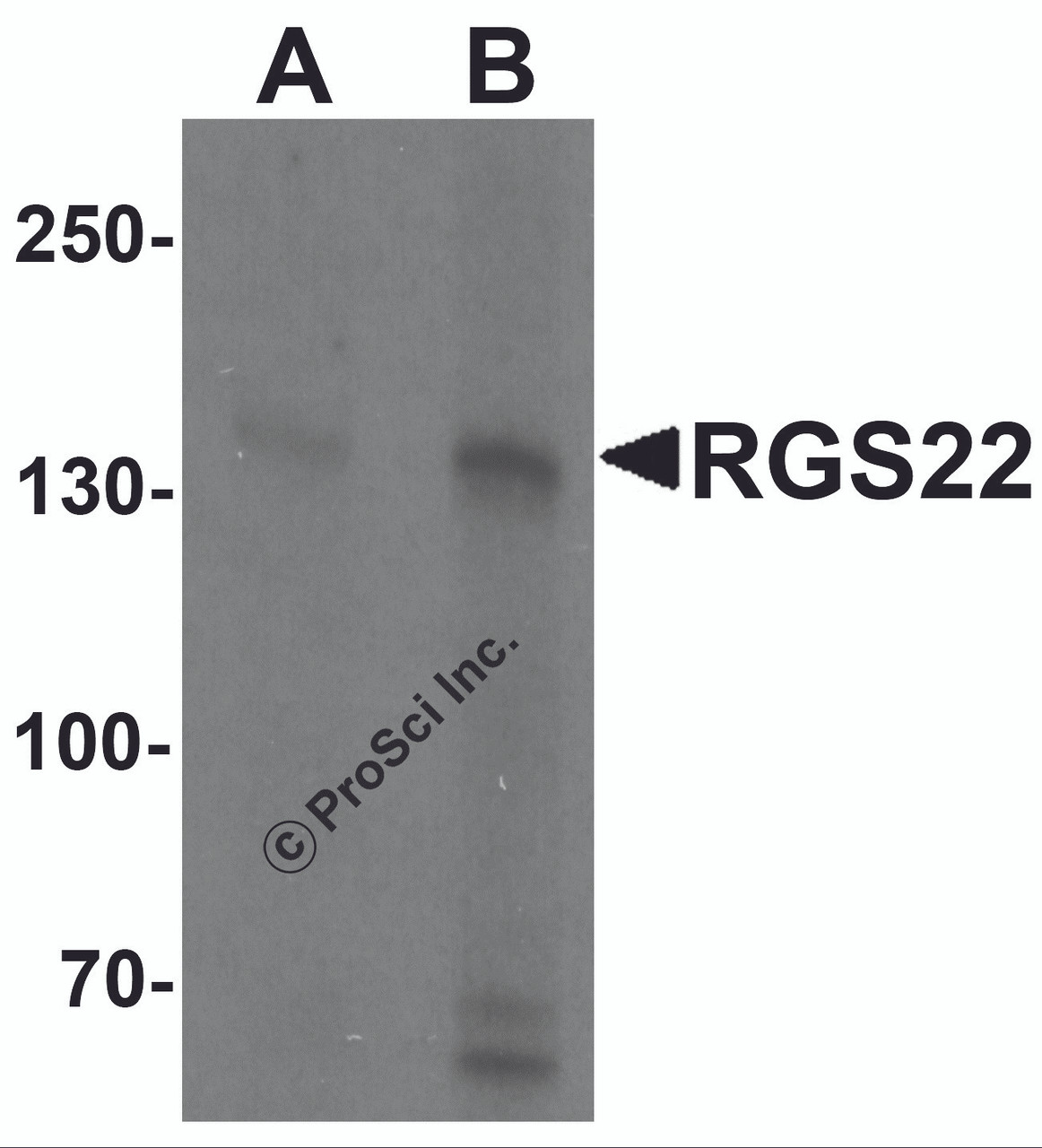
RGS22 Antibody | 7001 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: RGS22 antibody was raised against a 19 amino acid synthetic peptide near the amino terminus of human RGS22.
The immunogen is located within amino acids 870 - 920 of RGS22.
Research Area: Cancer, Cell Cycle
Tested Application: E, WB, IF
Application: RGS22 antibody can be used for detection of RGS22 by Western blot at 1 - 2 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples and Immunofluorescence in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: At least four isoforms of RGS22 are known to exist; this antibody will detect the three longest isoforms. RGS22 antibody is predicted to not cross-react with other RGS proteins
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1205 - Jurkat Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: Cat. No. 11-701 - Human Testis Tissue Slide
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: 139 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: RGS22 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: RGS22 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: RGS22 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: RGS22 Antibody: CT145, PRTD-NY2, Regulator of G-protein signaling 22, RGS22
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: RGS22 Antibody: Regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS) proteins contain an 120 amino acid conserved domain, termed the RGS domain, that acts as a GTPase-activating protein that acts to reduce the signal transmitted by the receptor-activated G-alpha subunit. RGS22 is a recently identified member of this family that localizes to the testis and can interact with guanine nucleotide binding proteins alpha 11, 12, and 13 (GNA11, GNA12, and GNA13) . While RGS22 has been postulated to play a role in spermiogenesis in the testis, it is also expressed in several cancer cell lines with an epithelial origin and associated with cancer metastasis. Its overexpression in a highly metastatic cancer causes a decrease in cell migration and a reduction of the invasive potential of the cells, suggesting that RGS22 may be a potential prognostic biomarker for metastasis.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL