Product Description
S1P1 Antibody | 4809 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Bovine: (86%)
Immunogen: S1P1 antibody was raised against a 14 amino acid synthetic peptide near the carboxy terminus of the human S1P1.
The immunogen is located within the last 50 amino acids of S1P1.
Research Area: Immunology
Tested Application: E, WB, IHC-P, IF
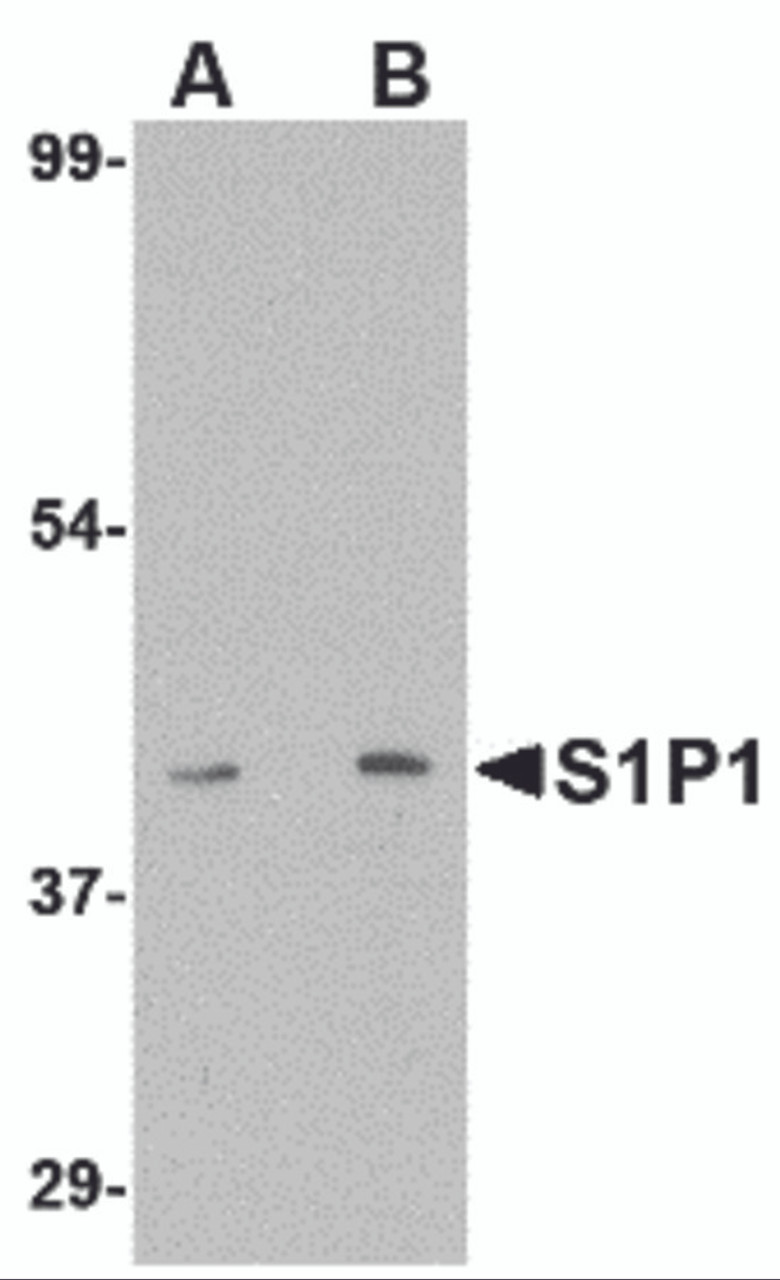
Application: S1P1 antibody can be used for detection of S1P1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2.5 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in mouse samples; Immunohistochemistry in mouse samples and Immunofluorescence in mouse samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: At least two isoforms of S1P1 are known to exist; this S1P1 antibody will only recognize the shorter isoform.
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1409 - Mouse Thymus Tissue Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Predicted: 42 kDa
Observed: 42 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: S1P1 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: S1P1 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: S1P1 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: S1P1 Antibody: EDG1, S1P1, CD363, ECGF1, EDG-1, CHEDG1, D1S3362, EDG1, Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1, Endothelial differentiation G-protein coupled receptor 1, S1P receptor 1
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: S1P1 Antibody: Movement of lymphocytes through lymphoid organs is required for generating immunity. Their migration into lymph nodes follows a series of events including integrin activation through chemokine signaling, adhesion and diapedis. The release of lymphocytes from lymph nodes is regulated by the phospholipid sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) . One of its receptors S1P1 binds S1P with high specificity and affinity; agonism of this receptor by the immunosuppressive agent FTY720 inhibits the entry of tissue T cells into afferent lymphatics in homeostatic and inflammatory conditions. Recent experiments have indicated that CCR7-deficient T cells left lymph nodes more rapidly than wild-type cells did and these cells where also less effectively retained after treatment with FTY720, and that egress competence could be restored by inactivating G alpha i-protein-coupled receptor signaling. These results suggest that S1P1 acts in the lymphocyte to promote lymph node egress by overcoming retention signals mediated by CCR7 and G alpha i-protein-coupled receptor signaling.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL