Product Description
CAPNS1 Antibody | 22-296 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 69-268 of human CAPNS1 (NP_001740.1) .
Research Area: Immunology, Neuroscience, Signal Transduction
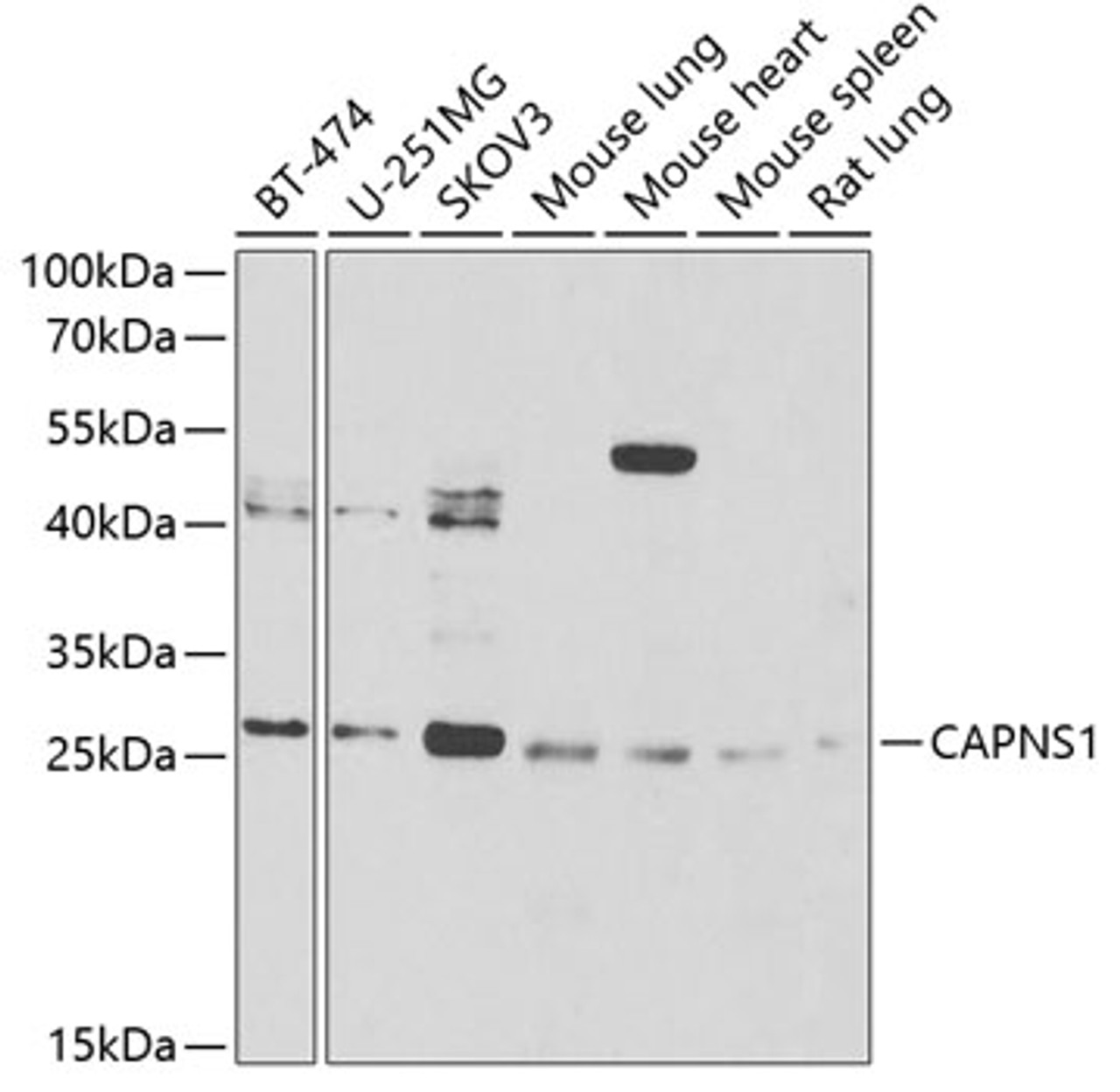
Tested Application: WB, IHC, IF
Application: WB: 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC: 1:50 - 1:100
IF: 1:50 - 1:100
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: BT-474
Positive Control 2: U-251MG
Positive Control 3: SKOV3
Positive Control 4: Mouse lung
Positive Control 5: Mouse heart
Positive Control 6: Mouse spleen
Molecular Weight: Observed: 28kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Affinity purification
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: Store at -20˚C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: CALPAIN4, CANP, CANPS, CAPN4, CDPS, CSS1, calpain small subunit 1, CANP small subunit, calcium-activated neutral proteinase small subunit, calcium-dependent protease small subunit 1, calcium-dependent protease, small subunit, calpain 4, small subunit (30K) , calpain regulatory subunit, calpain, small polypeptide, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: This gene is a member of the calpain small subunit family. Calpains are calcium-dependent cysteine proteinases that are widely distributed in mammalian cells. Calpains operate as heterodimers, comprising a specific large catalytic subunit (calpain 1 subunit in Calpain I, and calpain 2 subunit in Calpain II) , and a common small regulatory subunit encoded by this gene. This encoded protein is essential for the stability and function of both calpain heterodimers, whose proteolytic activities influence various cellular functions including apoptosis, proliferation, migration, adhesion, and autophagy. Calpains have been implicated in neurodegenerative processes, such as myotonic dystrophy. A pseudogene of this gene has been defined on chromosome 1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL









![CAPNS1 Antibody [AMM22329G] CAPNS1 Antibody [AMM22329G]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/870690/1162757/logo__92149.1659788186__31729.1659866802.png?c=2)
