Product Description
ESR1 Antibody | 26-058 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Antibody produced in rabbits immunized with a synthetic peptide corresponding a region of human ESR1.
Research Area: Transcription, Cell Cycle, Cancer, Signal Transduction, Immunology,
Tested Application: E, WB
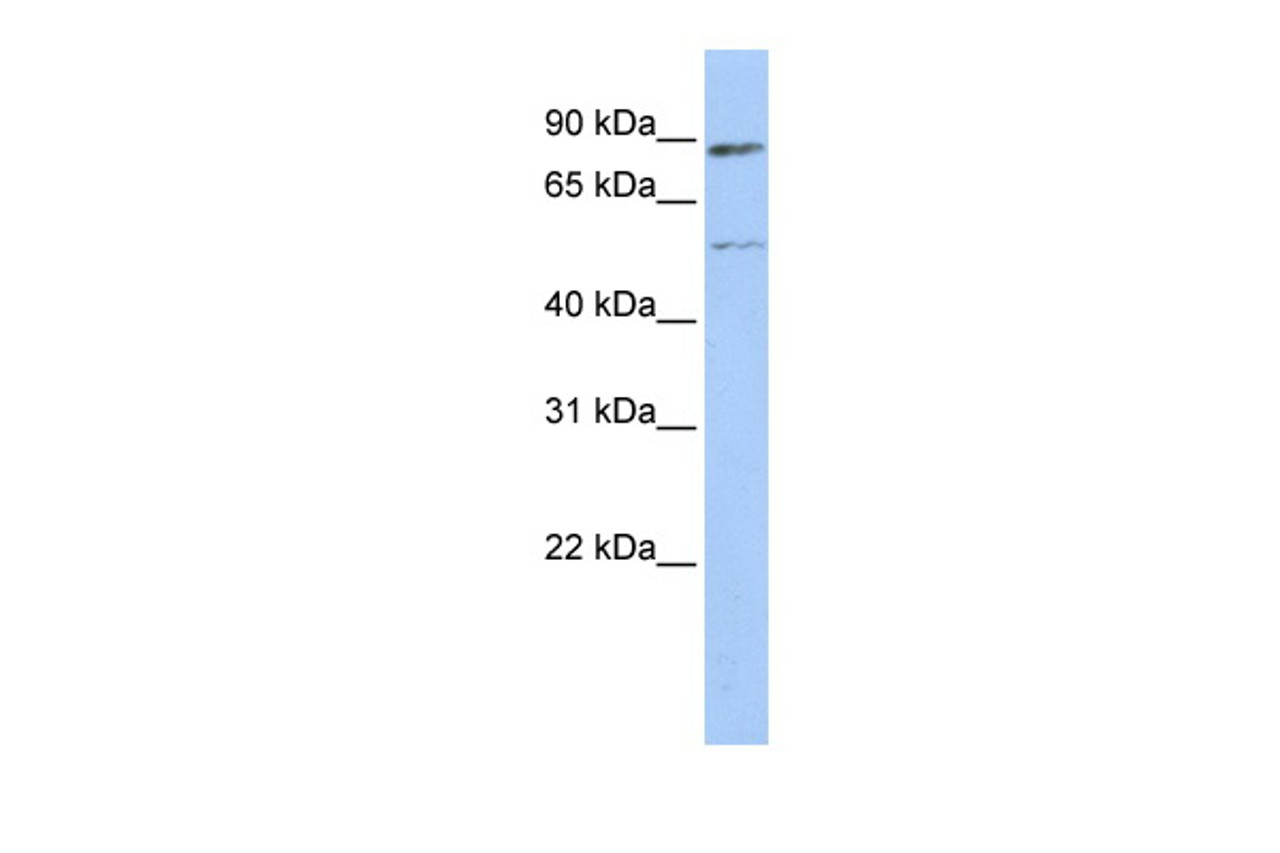
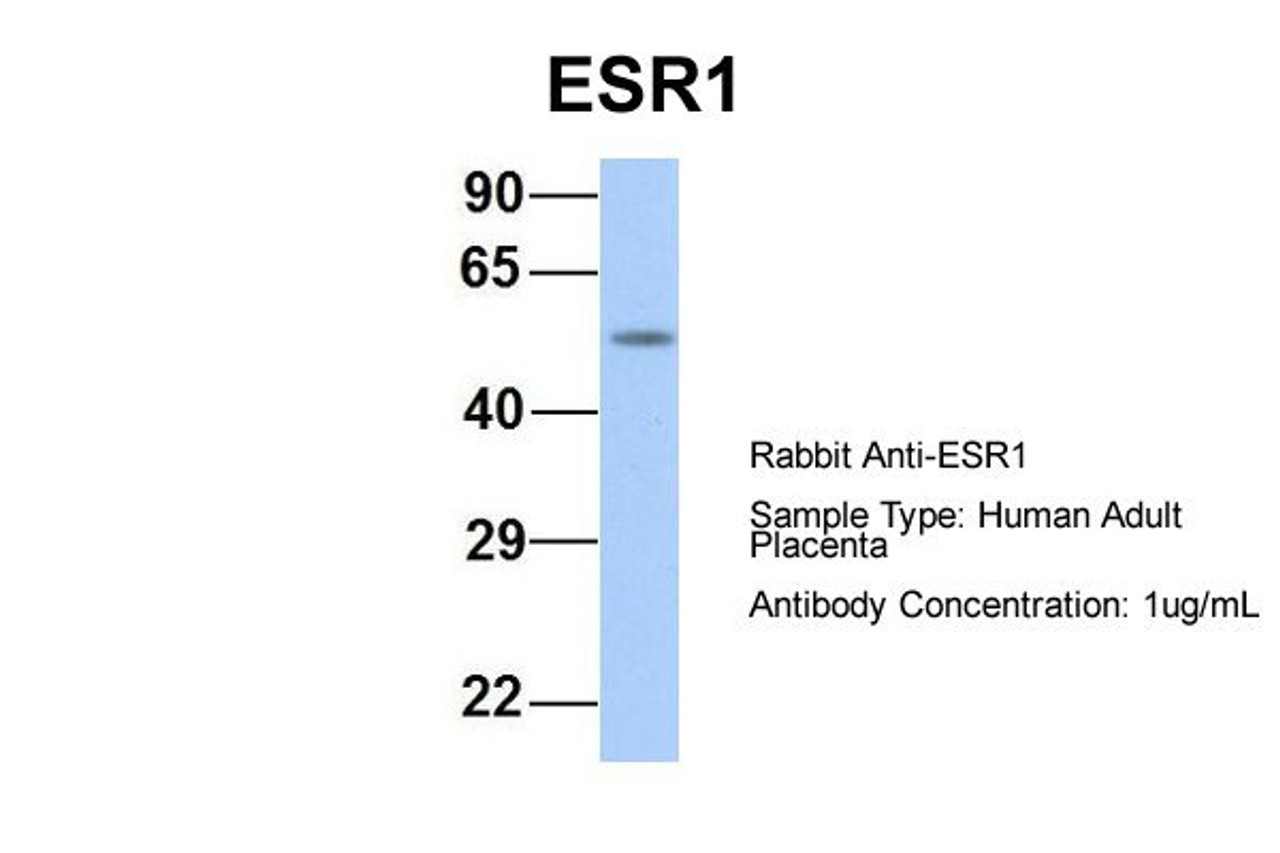
Application: ESR1 antibody can be used for detection of ESR1 by ELISA at 1:62500. ESR1 antibody can be used for detection of ESR1 by western blot at 1 μg/mL, and HRP conjugated secondary antibody should be diluted 1:50, 000 - 100, 000.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1201 - HeLa Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: 66 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Antibody is purified by peptide affinity chromatography method.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: N/A
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose.
Concentration: batch dependent
Storage Condition: For short periods of storage (days) store at 4˚C. For longer periods of storage, store ESR1 antibody at -20˚C. As with any antibody avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: ESR1, DKFZp686N23123, ER, ESR, ESRA, Era, NR3A1, ESTRR
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: Hairy/enhancer of split-related proteins, such as HEY1, are basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors implicated in cell fate decision and boundary formation. HEY genes are direct transcriptional targets of the Notch signaling pathways in Drosophila and vertebrates. This gene encodes an estrogen receptor, a ligand-activated transcription factor composed of several domains important for hormone binding, DNA binding, and activation of transcription. The protein localizes to the nucleus where it may form a homodimer or a heterodimer with estrogen receptor 2. Estrogen and its receptors are essential for sexual development and reproductive function, but also play a role in other tissues such as bone. Estrogen receptors are also involved in pathological processes including breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and osteoporosis. Alternative splicing results in several transcript variants, which differ in their 5' UTRs and use different promoters.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL