Product Description
HCLS1 Antibody | 27-647 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Antibody produced in rabbits immunized with a synthetic peptide corresponding a region of human HCLS1.
Research Area: Transcription, Signal Transduction, Immunology
Tested Application: E, WB
Application: HCLS1 antibody can be used for detection of HCLS1 by ELISA at 1:2500. HCLS1 antibody can be used for detection of HCLS1 by western blot at 1.25 μg/mL, and HRP conjugated secondary antibody should be diluted 1:50, 000 - 100, 000.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1205 - Jurkat Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
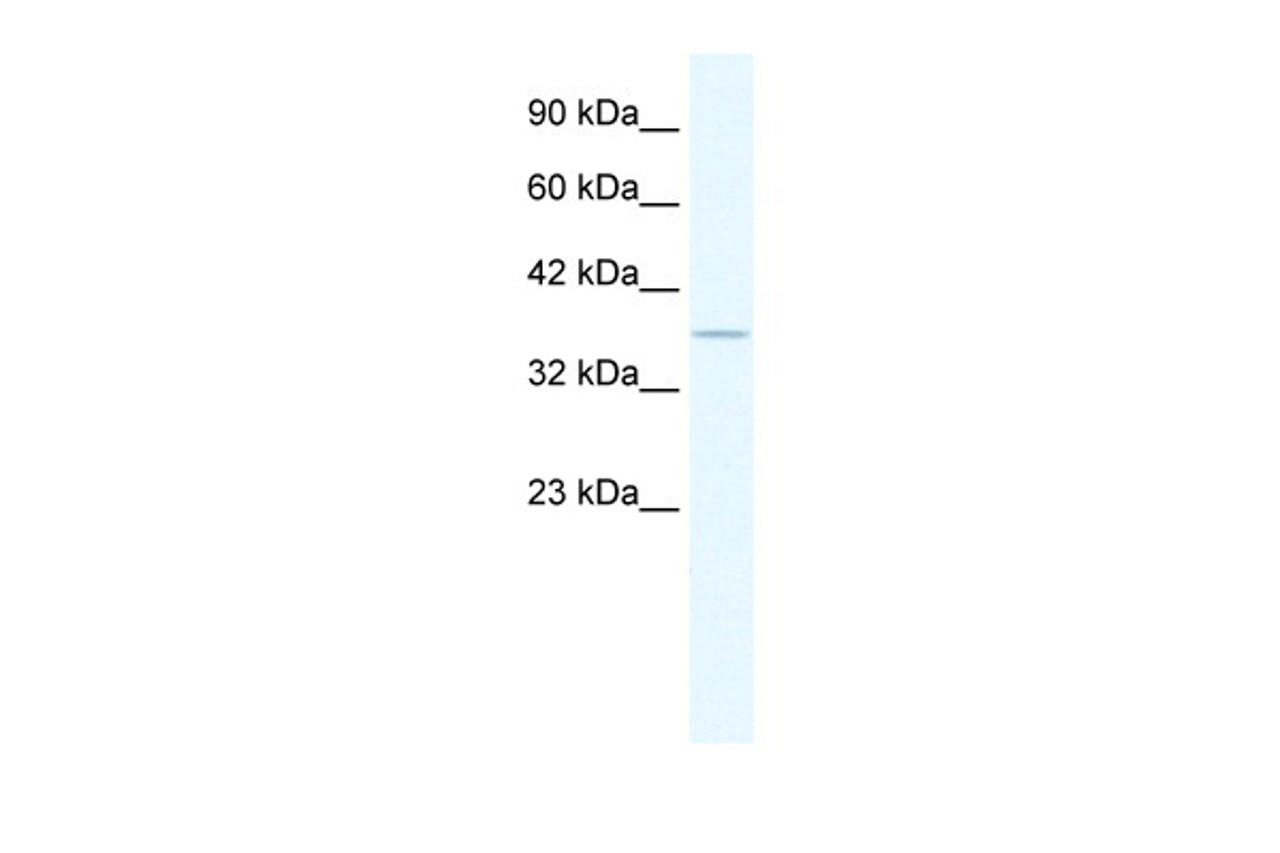
Molecular Weight: 54 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Antibody is purified by protein A chromatography method.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: N/A
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose.
Concentration: batch dependent
Storage Condition: For short periods of storage (days) store at 4˚C. For longer periods of storage, store HCLS1 antibody at -20˚C. As with any antibody avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: HCLS1, HS1, CTTNL
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: HS1 which is hematopoietic lineage cell-specific protein 1, is a substrate of protein tyrosine kinases in lymphocytes, it binds to F-actin, and promotes Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin polymerization. However, the mechanism for the interaction between HS1 and F-actin has not yet been fully characterized. HS1 contains 3.5 tandem repeats, a coiled-coil region, and an SH3 domain at the C terminus. Unlike cortactin, which is closely related to HS1 and requires absolutely the repeat domain for F-actin binding, an HS1 mutant with deletion of the repeat domain maintains a significant F-actin binding activity. Deletion of the coiled-coil region abolished the ability of HS1 to bind to actin filaments and to activate the Arp2/3 complex for actin nucleation and actin branching.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL