Product Description
RANTES Antibody | 19-765 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 24-91 of human RANTES (NP_002976.2) .
Research Area: Chemokines & Cytokines, Immunology, Innate Immunity, Neuroscience
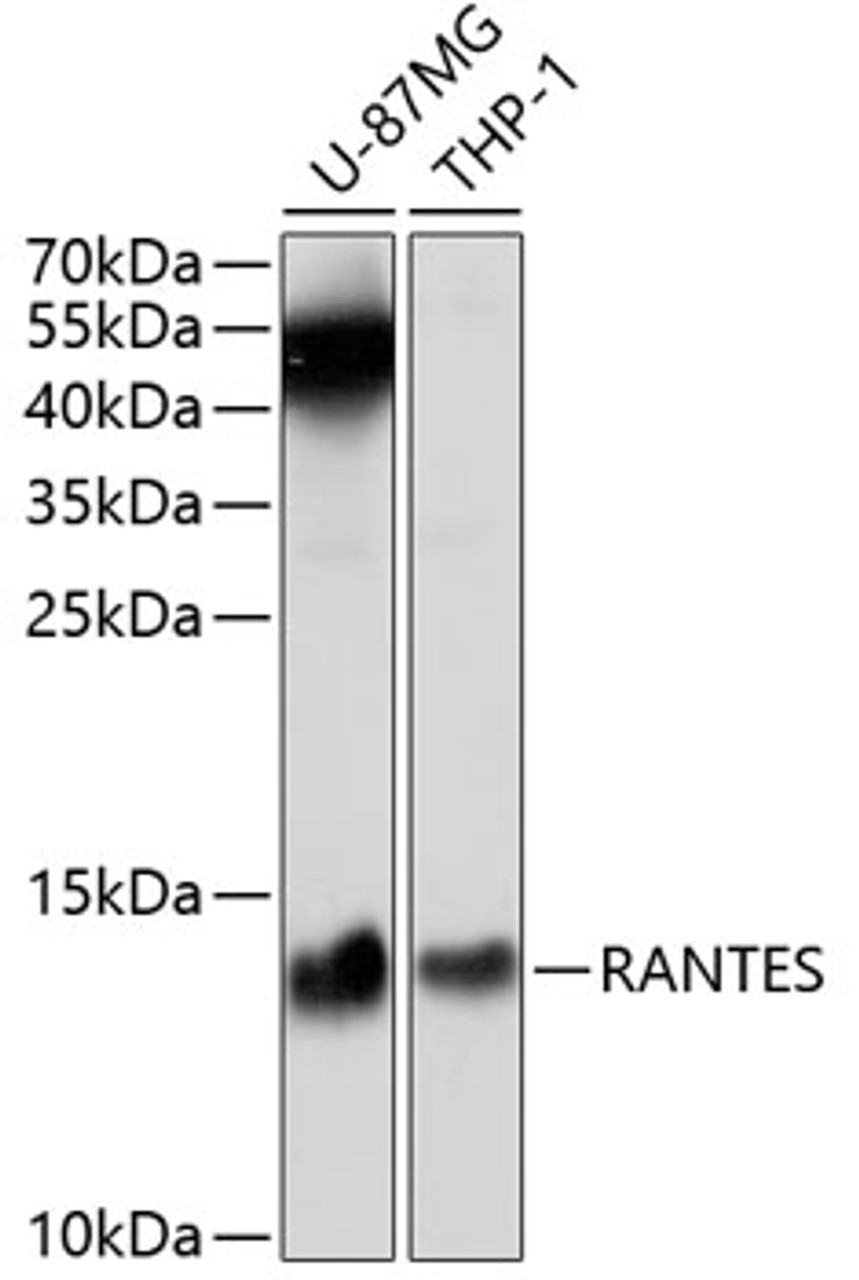
Tested Application: WB
Application: WB: 1:500 - 1:2000
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: U-87MG
Positive Control 2: THP-1
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Observed: 13kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Affinity purification
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: Store at -20˚C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: CCL5, Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5, D17S136E, EoCP, T-cell specific protein p288, SCYA5, SISd, T cell-specific protein P228, Beta-chemokine RANTES, C-C motif chemokine 5, RANTES, SIS-delta, Small-inducible cytokine A5, T-cell-specific protein RANTES, TCP228
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: This gene is one of several chemokine genes clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Chemokines form a superfamily of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of the N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine, a member of the CC subfamily, functions as a chemoattractant for blood monocytes, memory T helper cells and eosinophils. It causes the release of histamine from basophils and activates eosinophils. This cytokine is one of the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ cells. It functions as one of the natural ligands for the chemokine receptor chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 (CCR5) , and it suppresses in vitro replication of the R5 strains of HIV-1, which use CCR5 as a coreceptor. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different isoforms.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL