Product Description
CD36 Antibody [185-1G2] | 33-502 | ProSci
Host: Mouse
Reactivity: Human
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Stimulated human leukocytes were used as the immunogen for the CD36 antibody.
Research Area: Cancer, Immunology, Obesity, Signal Transduction
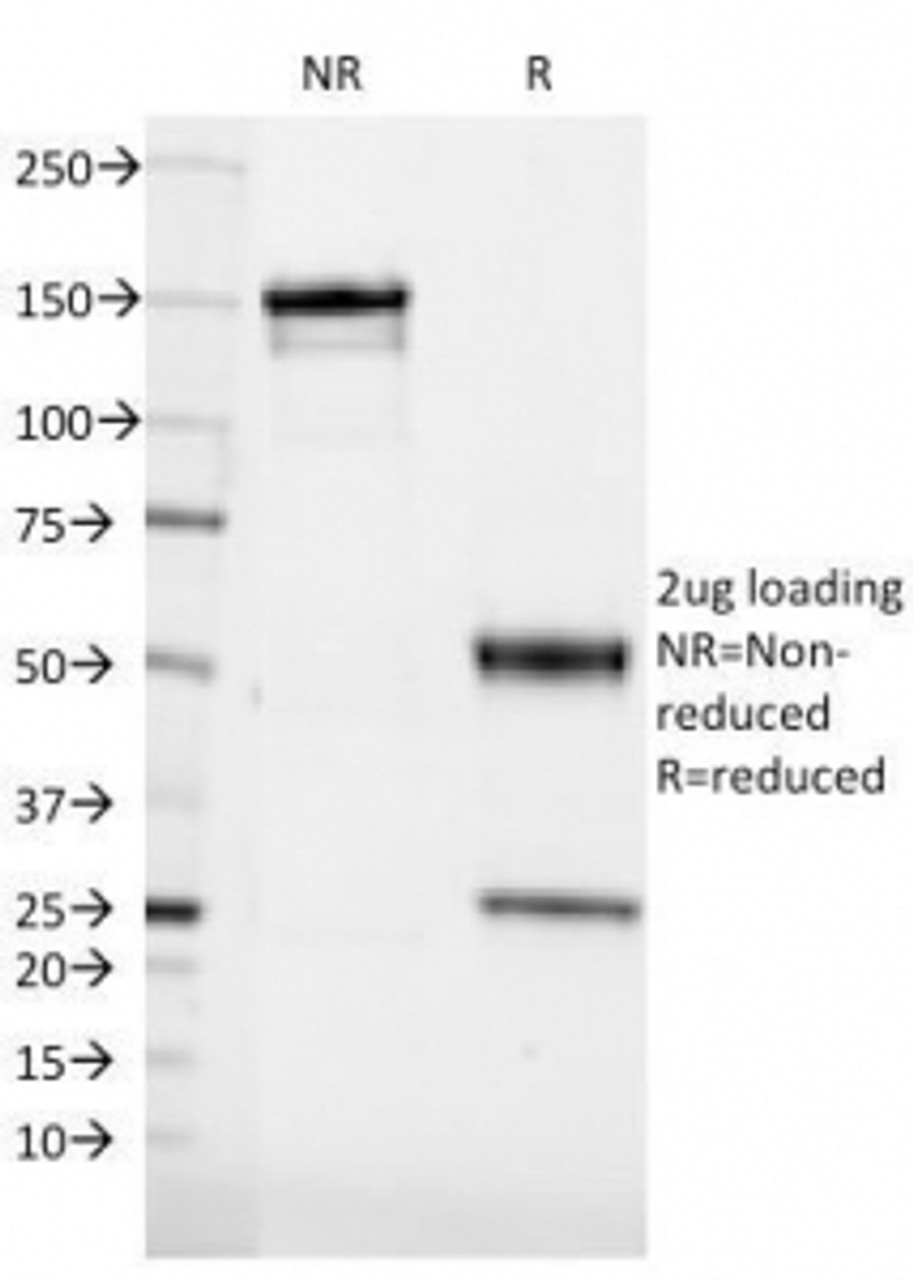
Tested Application: WB, Func, Flow, IF
Application: Functional Activity (Order SAF formulation) (1)
Flow Cytometry: 0.5-1 ug/million cells in 0.1ml
Immunofluorescence: 0.5-1 ug/ml
This mAb blocks adhesion of P. falciparum parasitized red blood cells to CD36 and strongly inhibits collagen-induced platelet aggregation.
Optimal dilution of the CD36 antibody should be determined by the researcher.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Protein G affinity chromatography
Clonality: Monoclonal
Clone: 185-1G2
Isotype: IgG2a, kappa
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.1 mg/ml BSA and 0.05% sodium azide
Concentration: 0.2 mg/mL
Storage Condition: Aliquot and Store at 2-8˚C. Avoid freez-thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: Platelet glycoprotein 4, Fatty acid translocase, FAT, Glycoprotein IIIb, GPIIIB, Leukocyte differentiation antigen CD36, PAS IV, PAS-4, Platelet collagen receptor, Platelet glycoprotein IV, GPIV, Thrombospondin receptor, CD36, CD36, GP3B, GP4
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher
BACKGROUND: CD36 binds to collagen, thrombospondin, anionic phospholipids and oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) . May function as a cell adhesion molecule. Directly mediates cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized erythrocytes. Binds long chain fatty acids and may function in the transport and/or as a regulator of fatty acid transport. Receptor for thombospondins, THBS1 AND THBS2, mediating their antiangiogenic effects. As a coreceptor for TLR4-TLR6 heterodimer, promotes inflammation in monocytes/macrophages. Upon ligand binding, such as oxLDL or amyloid-beta 42, rapidly induces the formation of a heterodimer of TLR4 and TLR6, which is internalized and triggers inflammatory response, leading to NF-kappa-B-dependent production of CXCL1, CXCL2 and CCL9 cytokines, via MYD88 signaling pathway, and CCL5 cytokine, via TICAM1 signaling pathway, as well as IL1B secretion. [UniProt]
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL

![CD36 Antibody [185-1G2] CD36 Antibody [185-1G2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/1280x1280/products/575339/811920/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__00736.1649091896.png?c=2)
![CD36 Antibody [185-1G2] CD36 Antibody [185-1G2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/100x100/products/575339/811920/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__00736.1649091896.png?c=2)

![CD36 Antibody [185-1G2] CD36 Antibody [185-1G2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/575339/811920/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__00736.1649091896.png?c=2)








