Product Description
KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11] | PM-6141 | ProSci
Host: Mouse
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: KLF4 antibody was raised against a 20 amino acid synthetic peptide near the carboxy terminus of human KLF4.
Research Area: Stem Cell
Tested Application: E, WB
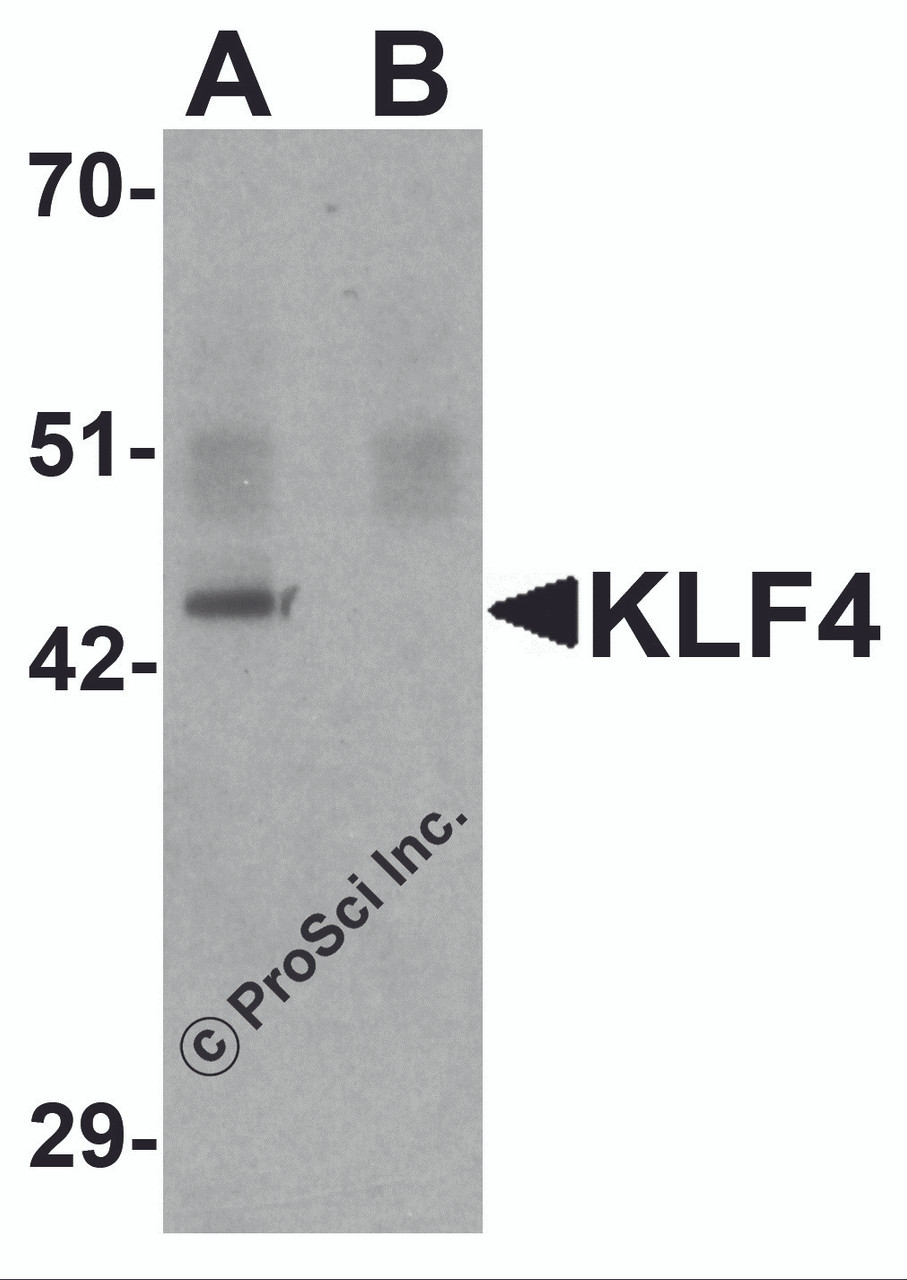
Application: KLF4 antibody can be used for detection of KLF4 by Western blot at 1 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in mouse samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: At least three isoforms of KLF4 are known to exist; this antibody will detect all three. KLF4 antibody will not cross-react with other Kruppel-like family members.
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1404 - Mouse Liver Tissue Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: KLF4 Monoclonal Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Monoclonal
Clone: 4G6E11
Isotype: IgG1
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: KLF4 Monoclonal Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: KLF4 monoclonal antibody can be stored at -20˚C, stable for one year.
Alternate Name: KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11] : EZF, GKLF
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: KLF4 Monoclonal Antibody: KLF4 is a transcription factor that functions as both a transcriptional activator and repressor to regulate proliferation and differentiation of multiple cell types. The role of KLF4 in embryonic development suggested that it might be useful in the creation of stem cells that might be useful in cell replacement therapies in the treatment of several degenerative diseases. Artificial stem cells, termed induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, can be created by expressing KLF4 and the transcription factors POU5F1, Sox2, and Lin28 along with c-Myc in mouse fibroblasts. More recently, experiments have demonstrated that iPS cells could be generated using expression plasmids expressing KLF4, Sox2, POU5F1 and c-Myc, eliminating the need for virus introduction, thereby addressing a safety concern for potential use of iPS cells in regenerative medicine. KLF4 interacts directly with POU5F1 and Sox2 in iPS and ES cells and activates the target gene NANOG.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL

![KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11] KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/1280x1280/products/552442/759607/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__04387.1649084825.png?c=2)
![KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11] KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/100x100/products/552442/759607/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__04387.1649084825.png?c=2)
![KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11] KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/552442/759607/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__04387.1649084825.png?c=2)

![KLF4 Antibody [4E5C3] KLF4 Antibody [4E5C3]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/552443/759609/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__14498.1649084825.png?c=2)


