Product Description
Alpha Internexin Antibody [1D2] | 50-250 | ProSci
Host: Mouse
Reactivity: Mammal
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Recombinant rat alpha-internexin expressed in and purified from E. coli.
Research Area: Neuroscience
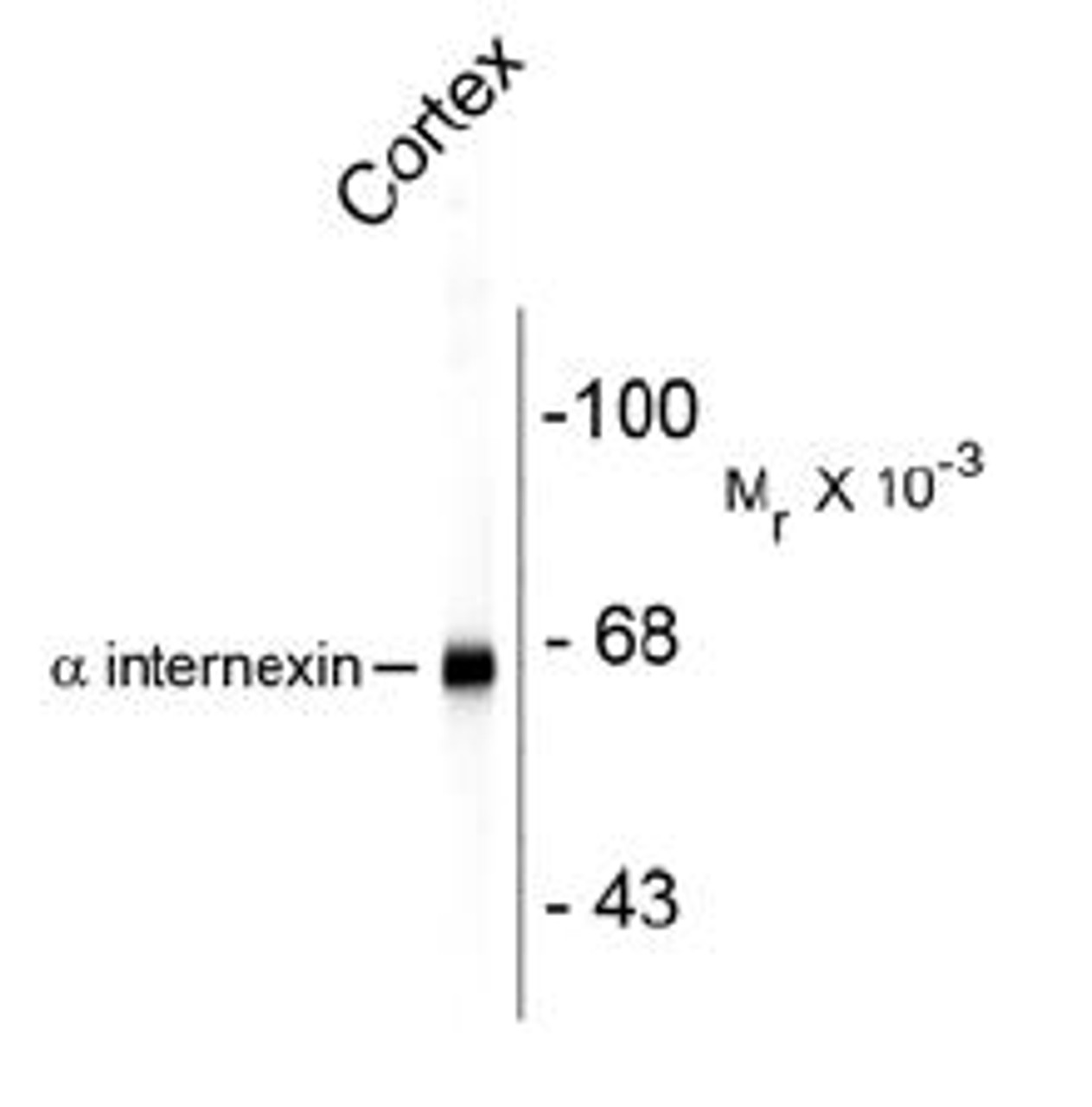
Tested Application: WB, IHC
Application: N/A
Specificiy: Specific for the ~66k alpha Internexin protein. Can be used on formalin-fixed cells in tissue culture, cryostat sections, and Western blotting. The epitope recognized by the ID2 clone is in the C-terminal non-helical extension of the protein and is unusually resistant to aldehyde fixation, so that this antibody is ideal for studies of paraffin embedded formalin fixed histological sections.
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: 66
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Total IgG fraction
Clonality: Monoclonal
Clone: 1D2
Isotype: N/A
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: N/A
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: Alpha Internexin antibody can be stored at -20˚C and is stable at -20˚C for at least 1 year.
Alternate Name: N/A
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: Alpha-internexin is a Class IV intermediate filament originally discovered as it co-purifies with other neurofilament subunits. Alpha-internexin is related to but distinct from the better known neurofilament triplet proteins, NF-L, NF-M and NF-H, having similar protein sequence motifs and a similar intron organization. It is expressed only in neurons and in large amounts early in neuronal development, but is down-regulated in many neurons as development proceeds. Many classes of mature neurons contain alpha-internexin in addition to NF-L, NF-M and NF-H. In some mature neurons alpha-internexin is the only neurofilament subunit expressed. Antibodies to alpha-internexin are therefore unique probes to study and classify neuronal types and follow their processes in sections and in tissue culture. In addition, recent studies show a marked up-regulation of alpha-internexin during neuronal regeneration. The use of antibodies to this protein in the study of brain tumors has not been examined to date, but is likely to be of interest. Recently Cairns et al. used this antibody to show that alpha-internexin is an abundant component of the inclusions of neurofilament inclusion body disease (NFID) , a serious human neurodegenerative disorder. The antibody was also used to confirm the presence of circulating auto-antibodies to alpha-internexin in the sera of some patients with endocrine autoimmunity, as well as in some normal individuals.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL

![Alpha Internexin Antibody [1D2] Alpha Internexin Antibody [1D2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/1280x1280/products/553214/761119/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__16676.1649086175.png?c=2)
![Alpha Internexin Antibody [1D2] Alpha Internexin Antibody [1D2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/100x100/products/553214/761119/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__16676.1649086175.png?c=2)

![Alpha Internexin Antibody [1D2] Alpha Internexin Antibody [1D2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/553214/761119/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__16676.1649086175.png?c=2)
![Neurofilament Alpha-Internexin / NF66 Antibody [1D2] | MC-999 Neurofilament Alpha-Internexin / NF66 Antibody [1D2] | MC-999](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/390923/569386/klogo__76714.1643661101__74217.1644059195.png?c=2)



