Product Description
p53 (phospho Ser37) Antibody | 79-448 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: p53 (Phospho-Ser37) antibody was raised against a peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 37 (L-P-S (p) -Q-A) derived from Human p53.
Research Area: Phospho-Specific, Apoptosis, Cancer, Cell Cycle
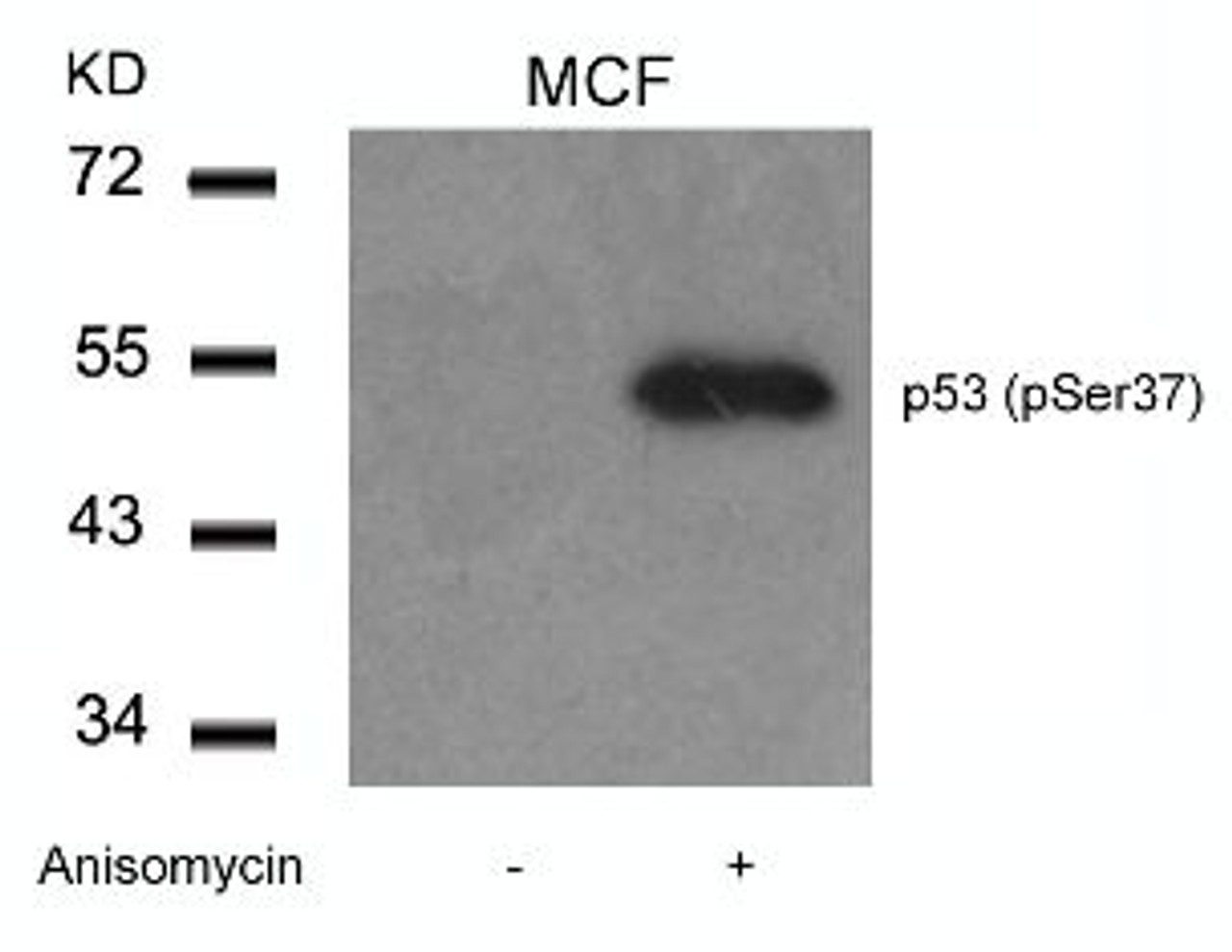
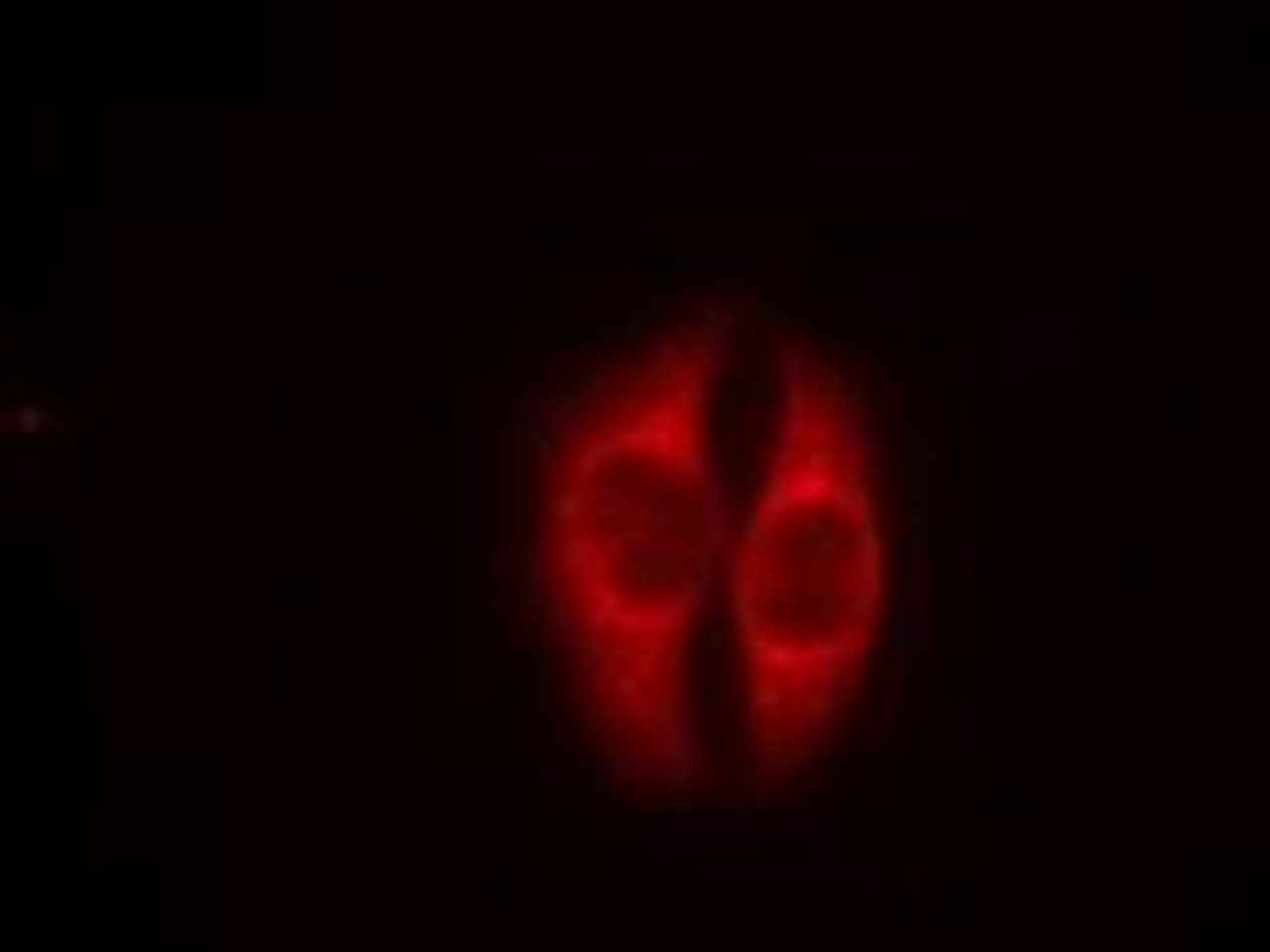
Tested Application: WB, IF
Application: Western Blot: 1:500~1:1000, Immunofluorescence: 1:100~1:200
Specificiy: This antibody detects endogenous level of p53 only when phosphorylated at serine 37.
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: 53 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy using non-phosphopeptide.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: N/A
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: Antibody supplied in phosphate buffered saline (without Mg2+ and Ca2+) , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: Store antibody at -20˚C for up to one year.
Alternate Name: P53, BCC7, LFS1, TRP53, GAD, GAD67, Tumor suppressor p53, Phosphoprotein p53, Antigen NY-CO-13, TP53
User Note: N/A
BACKGROUND: p53 is a nuclear protein which plays an essential role in the regulation of cell cycle specifically in the transition from G0 to G1. It is found in very low levels in normal cells however in a variety of transformed cell lines in high amounts and believed to contribute to transformation and malignancy. The open reading frame of p53 is 393 amino acids long, with the central region (consisting of amino acids from about 100 to 300) containing the DNA-binding domain. This proteolysis-resistant core is flanked by a C-terminal end mediating oligomerization and an N-terminal end containing a strong transcription activation signal. p53 binds as a tetramer to a PBS (p53-Binding Site) and activates the expression of downstream genes that inhibit growth and/or invasion. p53 binds as a tetramer to a p53-binding site (PBS) and to activate the expression of adjacent genes that inhibit growth and/or invasion. Deletion of one or both p53 alleles reduces the expression of tetramers, resulting in decreased expression of the growth inhibitory genes
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL