Product Description
LY6K Antibody | 6437 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: LY6K antibody was raised against an 18 amino acid synthetic peptide near the amino terminus of human LY6K.
The immunogen is located within the first 50 amino acids of LY6K.
Research Area: Cancer, Cell Cycle
Tested Application: E, WB
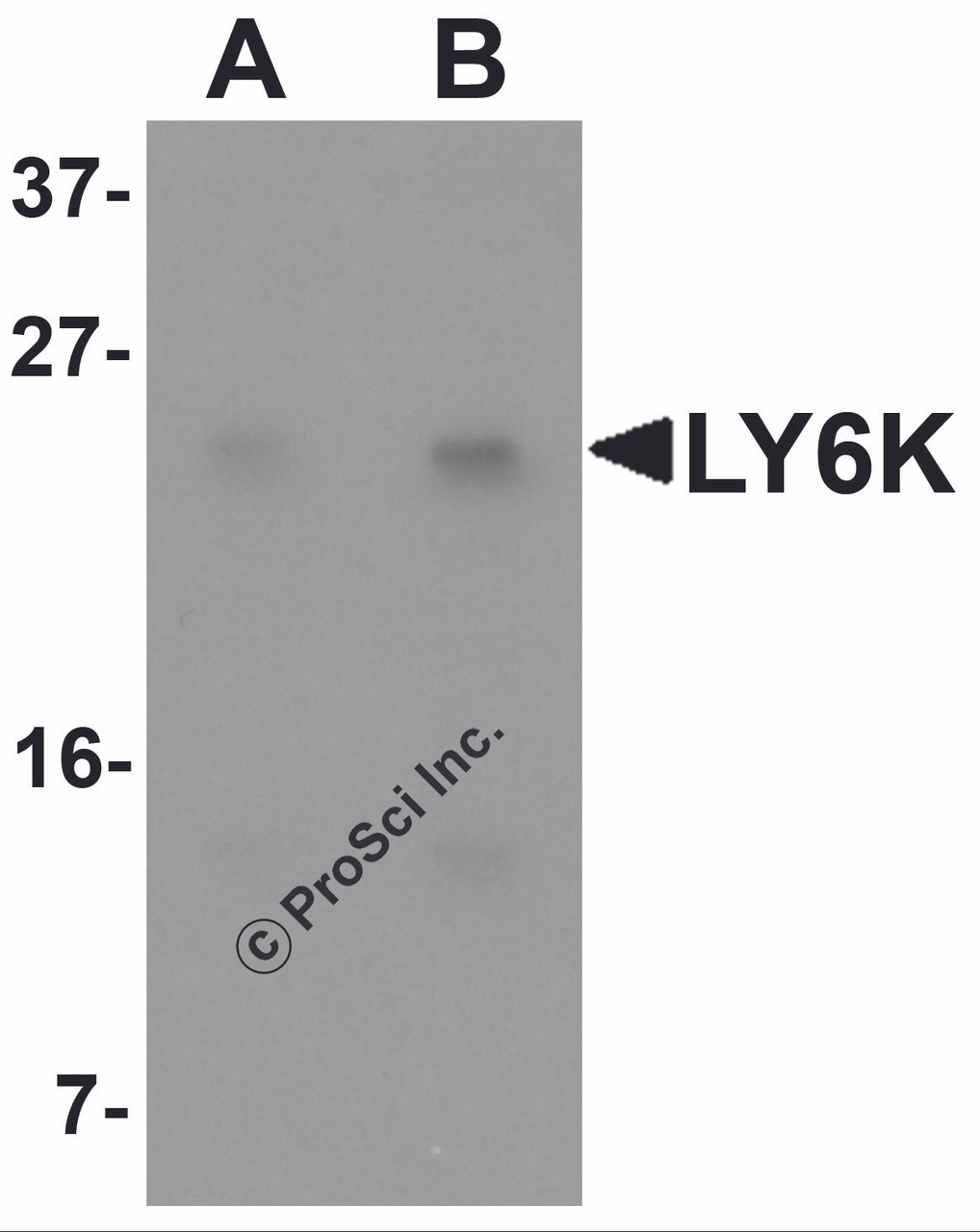
Application: LY6K antibody can be used for detection of LY6K by Western blot at 1 - 2 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: Multiple isoforms of LY6K are known to exist.
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1201 - HeLa Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: LY6K Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: LY6K Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: LY6K antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: LY6K Antibody: CT97, ly-6K, HSJ001348, CO16, Lymphocyte antigen 6K, Ly-6K
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: LY6K Antibody: The lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus K (LY6K) , a member of cancer-testis antigen was initially identified as a molecular marker for head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma as well a breast cancer. LY6K is a GPI-anchored membrane protein that is specifically associated with germ cell marker TEX101 and is strongly observed in testis, but only weakly in other tissues. LY6K mRNA was found to be upregulated in numerous bladder cancers due to gene amplification. Furthermore, knockdown experiments using LY6K siRNA reduced cell growth, migration and invasion in bladder carcinoma cell lines, suggesting that LY6K contributes to bladder cancer development.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL