Product Description
RUSC1 Antibody | 5411 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: RUSC1 antibody was raised against a 17 amino acid synthetic peptide from near the carboxy terminus of human RUSC1.
The immunogen is located within amino acids 780 - 830 of RUSC1.
Research Area: Innate Immunity
Tested Application: E, WB
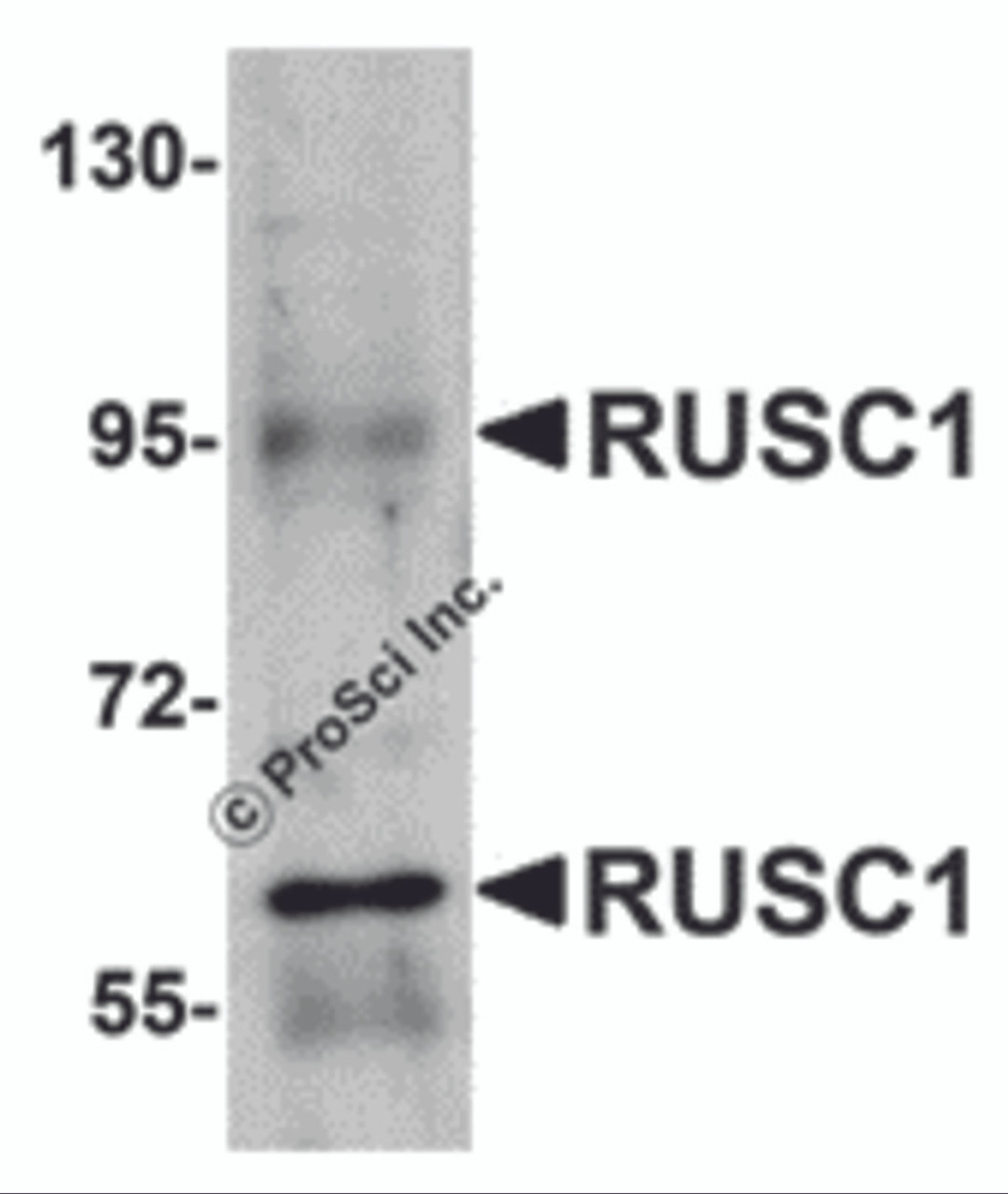
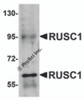
Application: RUSC1 antibody can be used for detection of RUSC1 by Western blot at 1 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in mouse samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1288 - A20 Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: RUSC1 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: RUSC1 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: RUSC1 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: RUSC1 Antibody: NESCA, NESCA, RUN and SH3 domain-containing protein 1, New molecule containing SH3 at the carboxy-terminus, Nesca
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: RUSC1 Antibody: RUSC1, also known as NESCA, shares with the related protein RUSC2 a common domain structure of RUN, leucine zipper and SH3 domain in addition to over 30% amino acid identity. RUSC1 is an adapter protein that can bind to the TrkA receptor and is necessary in the NGF-induced neurite growth of PC12 cells. RUSC1 has also been shown to interact with IκB kinase- (IKK-) gamma, the regulatory subunit of the IKK complex that is required for NF-κB activation in many signaling pathways such as TNF-R or the TLR pathways. RUSC1 can also bind to the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF6, which then catalyzes RUSC1 polyubiquitination. Since overexpression of RUSC1 strongly inhibits TRAF6-mediated polyubiquitination of IKK-gamma, RUSC1 may be a link in the IKK-gamma-mediated NF-κB activation pathway.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL