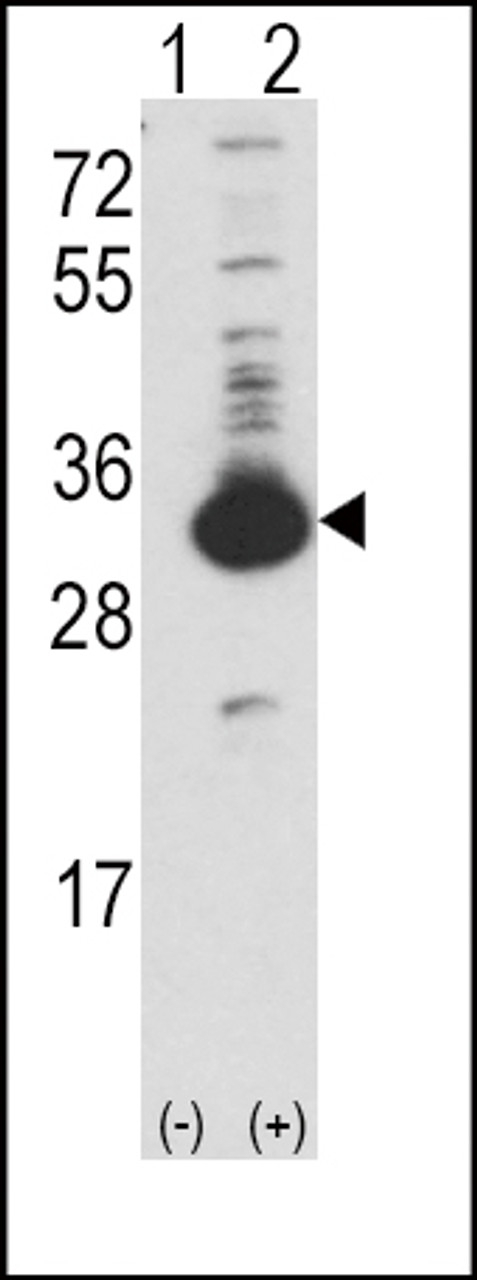
Product Description
Ketohexokinase Antibody | 62-632 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Rat
Immunogen: This Ketohexokinase (KHK) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 18-46 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human Ketohexokinase (KHK) .
Research Area: Cancer, Obesity, Signal Transduction
Tested Application: WB
Application: For WB starting dilution is: 1:1000
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: 33 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: Rabbit Ig
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: Supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide.
Concentration: batch dependent
Storage Condition: Store at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: Ketohexokinase, Hepatic fructokinase, KHK
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: Ketohexokinase (KHK) , or fructokinase, catalyzes conversion of fructose to fructose-1-phosphate. Splice variant 1 is the highly active form found in liver, renal cortex, and small intestine, while splice variant 2 is the lower activity form found in most other tissues. KHK, like glucokinase (GCK) and glucokinase regulator (GCKR) , is present in both liver and pancreatic islets. The inhibition of GCK by GCKR is blocked by binding of fructose-1-phosphate to GCKR. The chromosomal proximity of the metabolically connected GCKR and KHK genes has a genetic linkage in type 2 diabetes. Fructosuria, or hepatic fructokinase deficiency, is a benign, asymptomatic defect of intermediary metabolism associated with heterozygosity for G50R and A43T mutations in KHK.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL