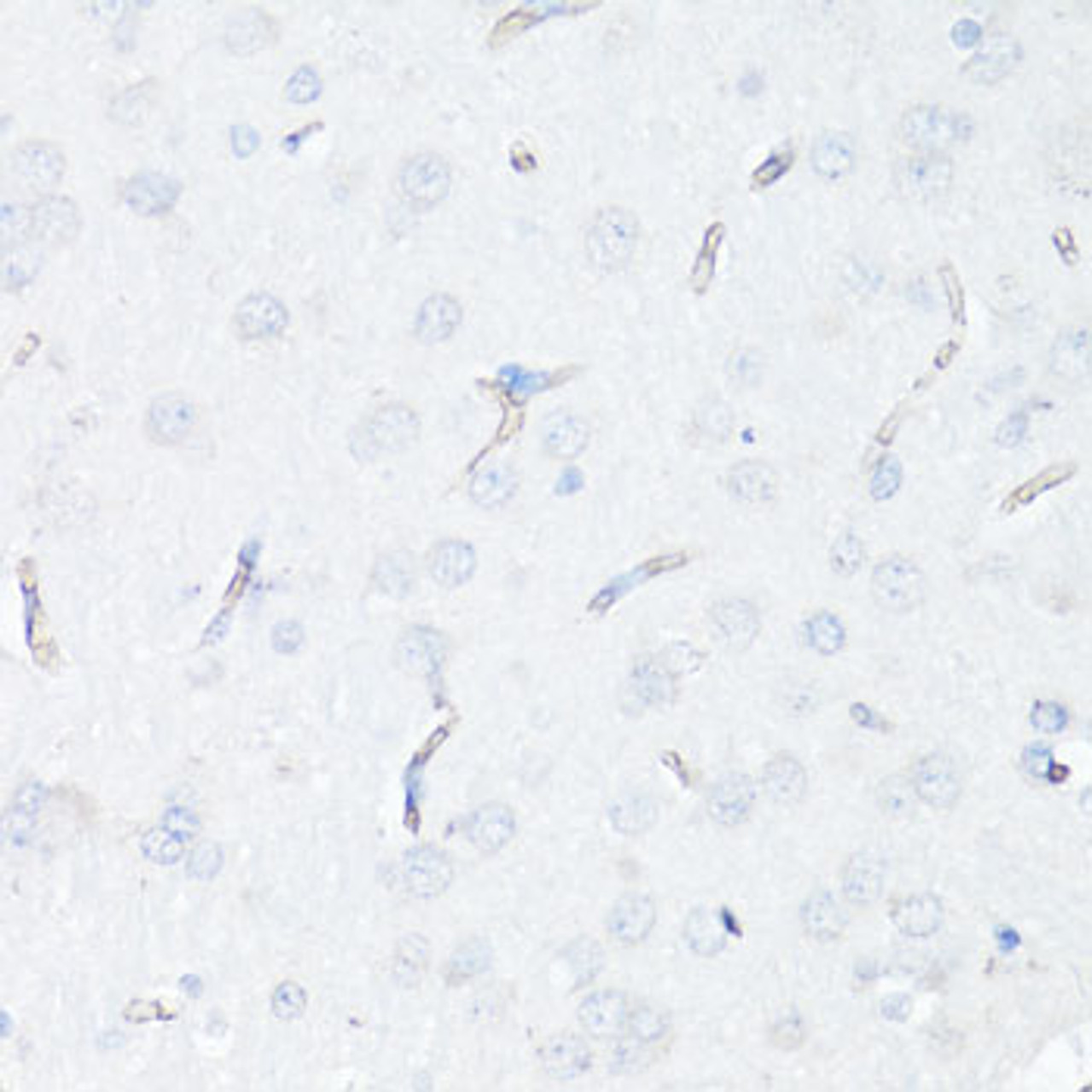
Product Description
P Glycoprotein Antibody | 14-133 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 600-700 of human P Glycoprotein (NP_000918.2) .
Research Area: Cancer, Immunology, Signal Transduction, Stem Cell
Tested Application: WB, IHC, IF
Application: WB: 1:500 - 1:1000
IHC: 1:50 - 1:200
IF: 1:50 - 1:200
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: 293T
Positive Control 2: Mouse heart
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Observed: 180kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Affinity purification
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: Store at -20˚C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: ABCB1, ABC20, Abcb1b, CLCS, Colchicin sensitivity, CD243, Doxorubicin resistance, IBD13, gp170, MDR1, Multidrug resistance protein 1, P glycoprotein, P-glycoprotein 1, P-GP, CD243 antigen, PGY1
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: The membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White) . This protein is a member of the MDR/TAP subfamily. Members of the MDR/TAP subfamily are involved in multidrug resistance. The protein encoded by this gene is an ATP-dependent drug efflux pump for xenobiotic compounds with broad substrate specificity. It is responsible for decreased drug accumulation in multidrug-resistant cells and often mediates the development of resistance to anticancer drugs. This protein also functions as a transporter in the blood-brain barrier. Mutations in this gene are associated with colchicine resistance and Inflammatory bowel disease 13. Alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL