Product Description
RBPMS Antibody | 29-238 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Antibody produced in rabbits immunized with a synthetic peptide corresponding a region of human RBPMS.
Research Area: Other
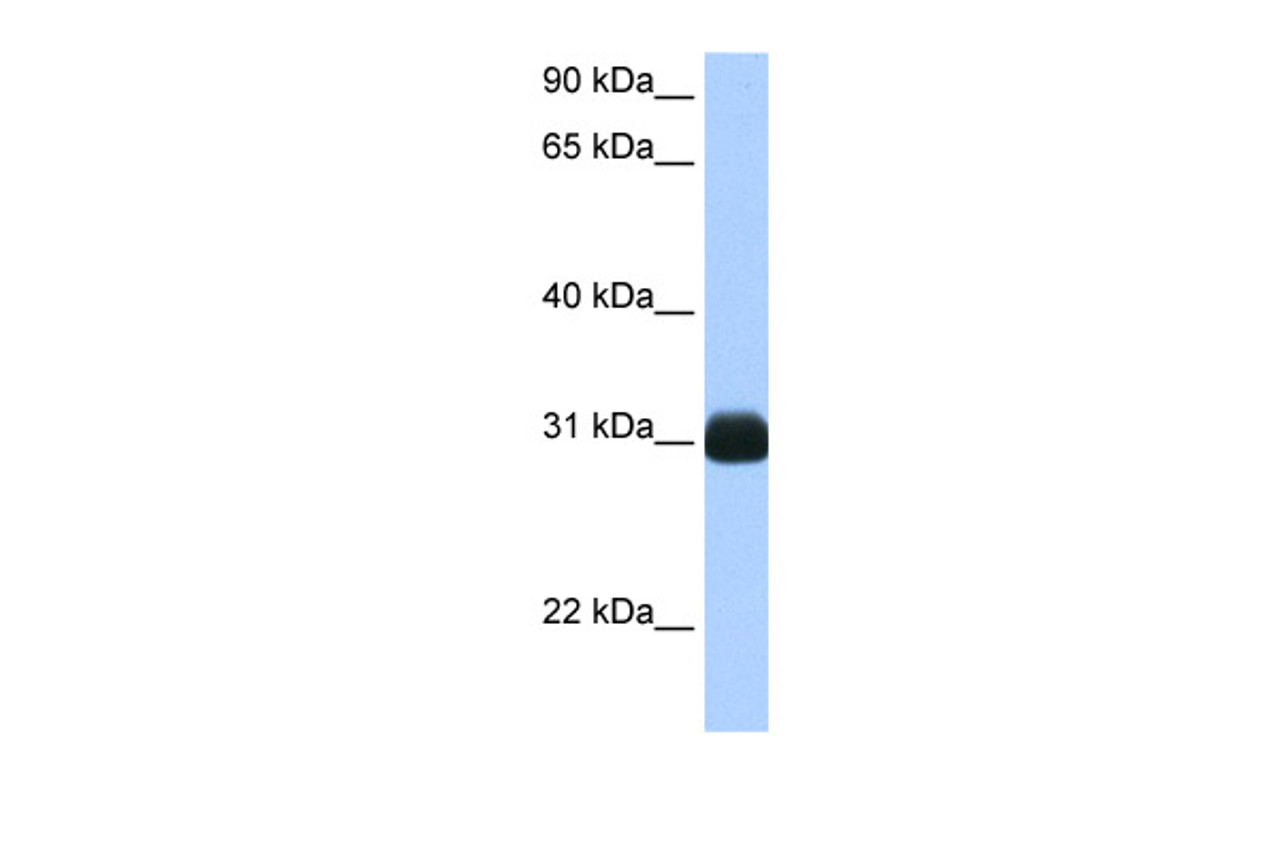
Tested Application: E, WB
Application: RBPMS antibody can be used for detection of RBPMS by ELISA at 1:62500. RBPMS antibody can be used for detection of RBPMS by western blot at 0.5 μg/mL, and HRP conjugated secondary antibody should be diluted 1:50, 000 - 100, 000.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1304 - Human Liver Tissue Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: 24 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Antibody is purified by peptide affinity chromatography method.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: N/A
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose.
Concentration: batch dependent
Storage Condition: For short periods of storage (days) store at 4˚C. For longer periods of storage, store RBPMS antibody at -20˚C. As with any antibody avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: RBPMS, HERMES
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: RBPMS is a member of the RRM family of RNA-binding proteins. The RRM domain is between 80-100 amino acids in length and family members contain one to four copies of the domain. The RRM domain consists of two short stretches of conserved sequence called RNP1 and RNP2, as well as a few highly conserved hydrophobic residues. RBPMS has a single, putative RRM domain in its N-terminus. This gene encodes a member of the RRM family of RNA-binding proteins. The RRM domain is between 80-100 amino acids in length and family members contain one to four copies of the domain. The RRM domain consists of two short stretches of conserved sequence called RNP1 and RNP2, as well as a few highly conserved hydrophobic residues. The protein encoded by this gene has a single, putative RRM domain in its N-terminus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL