Product Description
IL-10 Antibody (biotin) | XP-5163Bt | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Produced from sera of rabbits pre-immunized with highly pure (>98%) recombinant rat IL-10 (Rat Interleukin-10) .
Research Area: Immunology, Chemokines & Cytokines, Antibody Pairs
Tested Application: E, WB
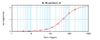
Application: ELISA:
Sandwich:
To detect Rat IL-10 by sandwich ELISA (using 100 μL/well antibody solution) a concentration of 0.25 - 1.0 μg/mL of this antibody is required. This biotinylated polyclonal antibody, in conjunction with our Polyclonal Anti-Rat IL-10 (XP-5163) as a capture antibody, allows the detection of at least 0.2 - 0.4 ng/well of recombinant Rat IL-10.
Western Blot:
To detect rat IL-10 by Western Blot analysis this antibody can be used at a concentration of 0.1 - 0.2 μg/mL. Used in conjunction with compatible secondary reagents the detection limit for recombinant rat IL-10 is 1.5 - 3.0 ng/lane, under either reducing or non-reducing conditions.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Anti-rat IL-10 specific antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and then biotinylated.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: N/A
Conjugate: Biotin
Physical State: Lyophilized
Buffer: N/A
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: IL-10 antibody is stable for at least 2 years from date of receipt at -20˚C. The reconstituted antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-8˚C. Frozen aliquots are stable for at least 6 months when stored at -20˚C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: IL10X, Il-10, Interleukin-10, Cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor, IL-10
User Note: Centrifuge vial prior to opening.
BACKGROUND: Interleukins (ILs) are a large group of cytokines that are produced mainly by leukocytes, although some are produced by certain phagocytes and auxiliary cells. ILs have a variety of functions, but most function to direct other immune cells to divide and differentiate. Each IL acts on a specific, limited group of cells through a receptor specific for that IL.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL