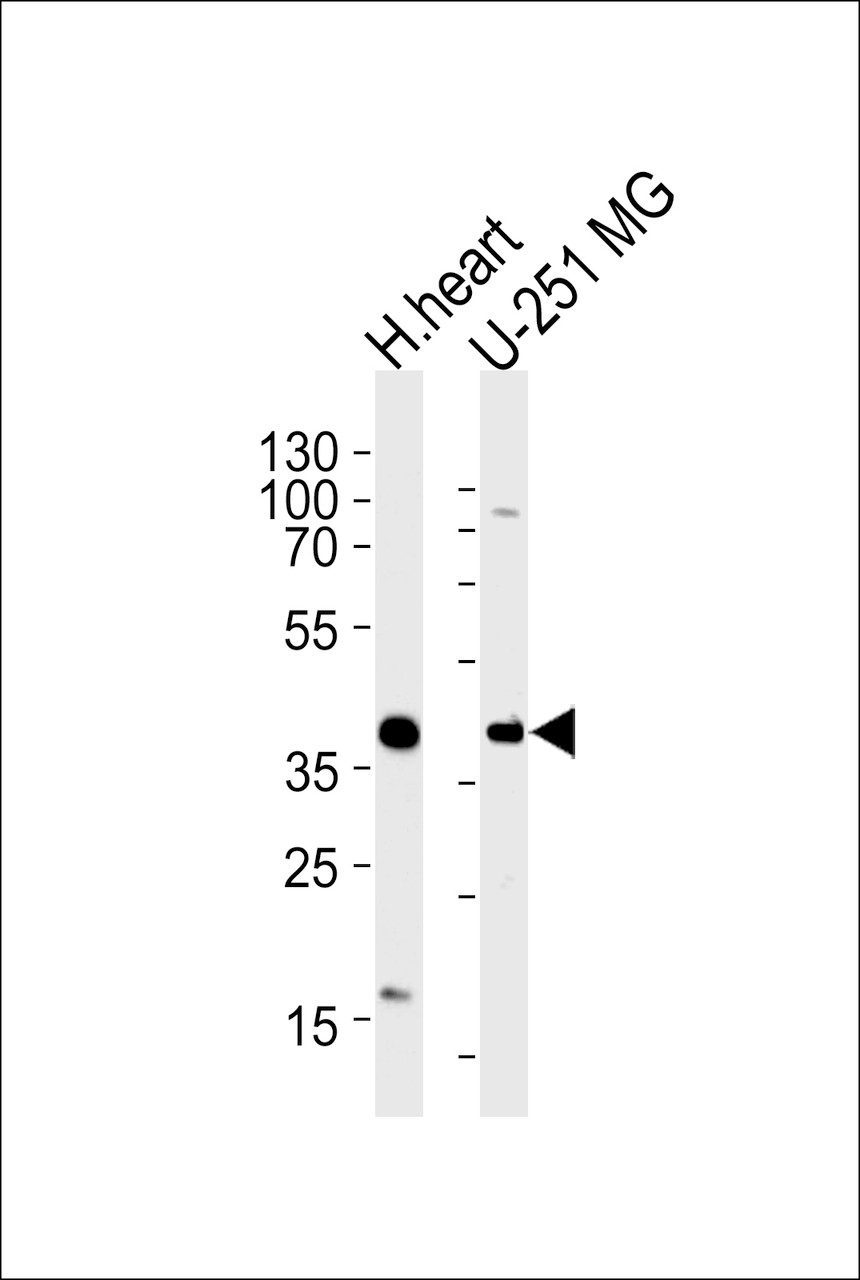
Product Description
AKTIP Antibody | 60-501 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Chicken, Monkey, Mouse, Rat
Immunogen: This AKTIP antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 262-288 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human AKTIP.
Research Area: Signal Transduction
Tested Application: WB
Application: For WB starting dilution is: 1:1000
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: 33 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: Rabbit Ig
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: Supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide.
Concentration: batch dependent
Storage Condition: Store at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: AKT-interacting protein, Ft1, Fused toes protein homolog, AKTIP, FTS
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: The mouse homolog of this gene produces fused toes and thymic hyperplasia in heterozygous mutant animals while homozygous mutants die in early development. This gene may play a role in apoptosis as these morphological abnormalities are caused by altered patterns of programmed cell death. The protein encoded by this gene is similar to the ubiquitin ligase domain of other ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes but lacks the conserved cysteine residue that enables those enzymes to conjugate ubiquitin to the target protein. This protein interacts directly with serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B (PKB) /Akt and modulates PKB activity by enhancing the phosphorylation of PKB's regulatory sites. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding the same protein.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL