Product Description
SHISA4 Antibody | 7277 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: SHISA4 antibody was raised against a 15 amino acid peptide near the center of human SHISA4 .
The immunogen is located within amino acids 100 - 150 of SHISA4.
Research Area: Stem Cell
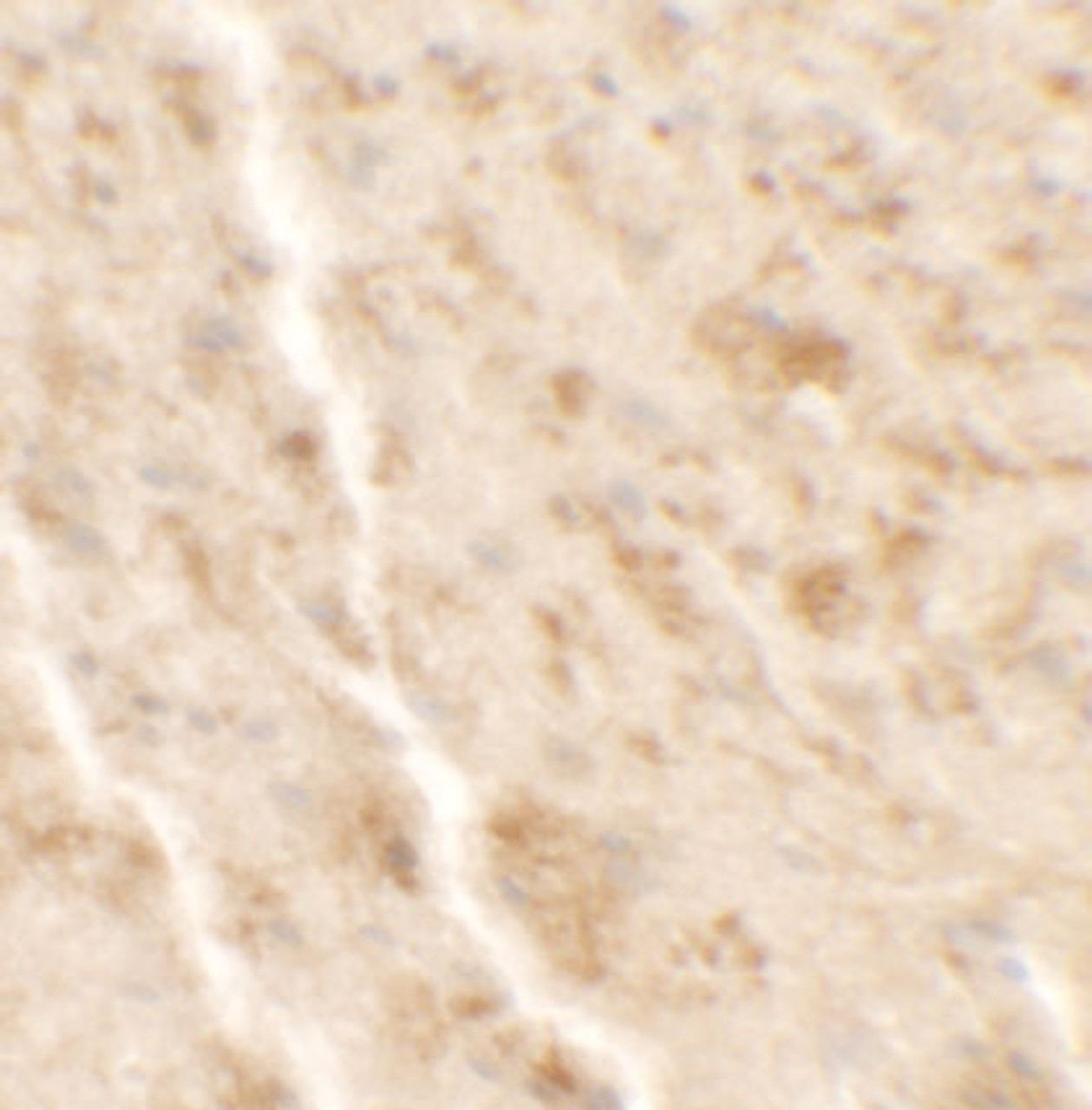
Tested Application: E, WB, IHC-P, IF
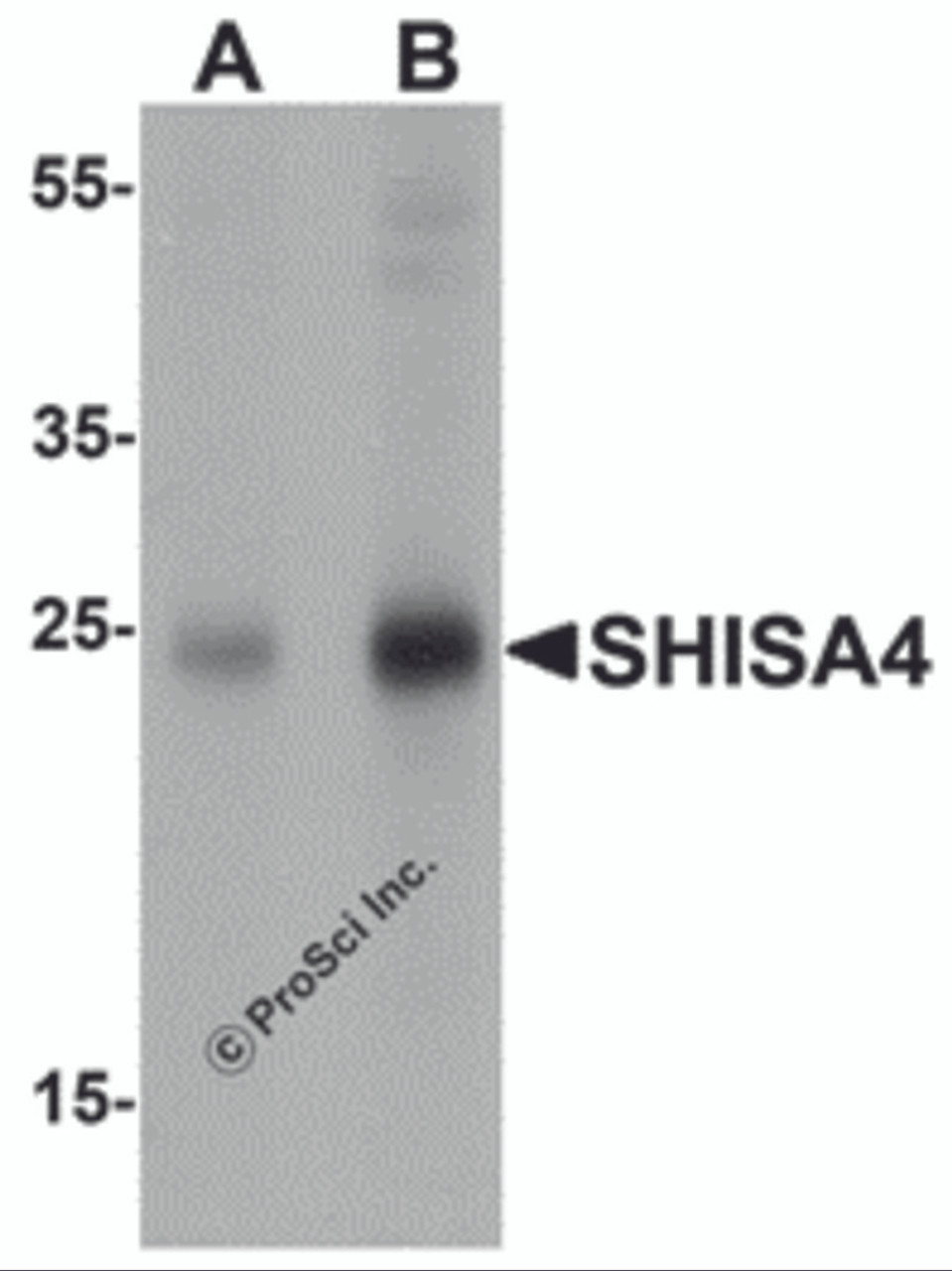
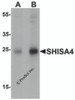
Application: SHISA4 Antibody can be used for detection of SHISA4 by Western blot starting at 1 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples; Immunohistochemistry in mouse samples and Immunofluorescence in mouse samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: SHISA4 antibody is predicted to not cross-react with other SHISA protein family members.
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1303 - Human Brain Tissue Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
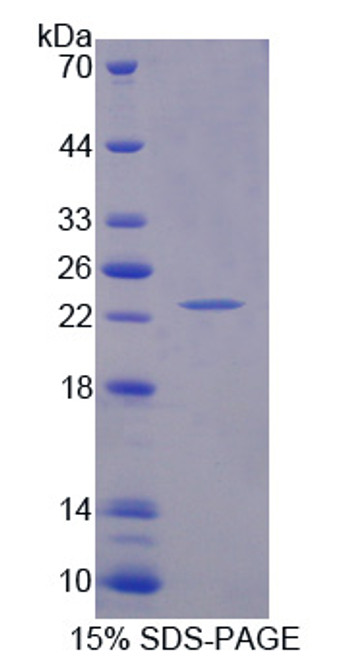
Molecular Weight: Predicted: 22 kDa
Observed: 24 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: SHISA4 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: SHISA4 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: SHISA4 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year.
Alternate Name: SHISA4 Antibody: TMEM58, C1orf40, TMEM58, UNQ583/PRO1153, Protein shisa-4, Transmembrane protein 58
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: SHISA4 Antibody: SHISA4 plays an essential role in the maturation of presomitic mesoderm cells by individual attenuation of both FGF and WNT signaling. The Shisa family of single-transmembrane proteins is characterized by an N-terminal cysteine-rich domain and a proline-rich C-terminal region. Its founding member, Xenopus Shisa, promotes head development by antagonizing Wnt and FGF signaling. Shisa physically interacted with immature forms of the Wnt receptor Frizzled and the FGF receptor within the ER and inhibited their posttranslational maturation and trafficking to the cell surface. Loss of Shisa function sensitized the neuroectoderm to Wnt signaling and suppressed head formation during gastrulation.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL