Product Description
ZNF687 Antibody | 6861 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Mouse: (82%)
Immunogen: ZNF687 antibody was raised against a 17 amino acid synthetic peptide near the carboxy terminus of human ZNF687.
The immunogen is located within amino acids 1160 - 1210 of ZNF687.
Research Area: Stem Cell
Tested Application: E, WB, IF
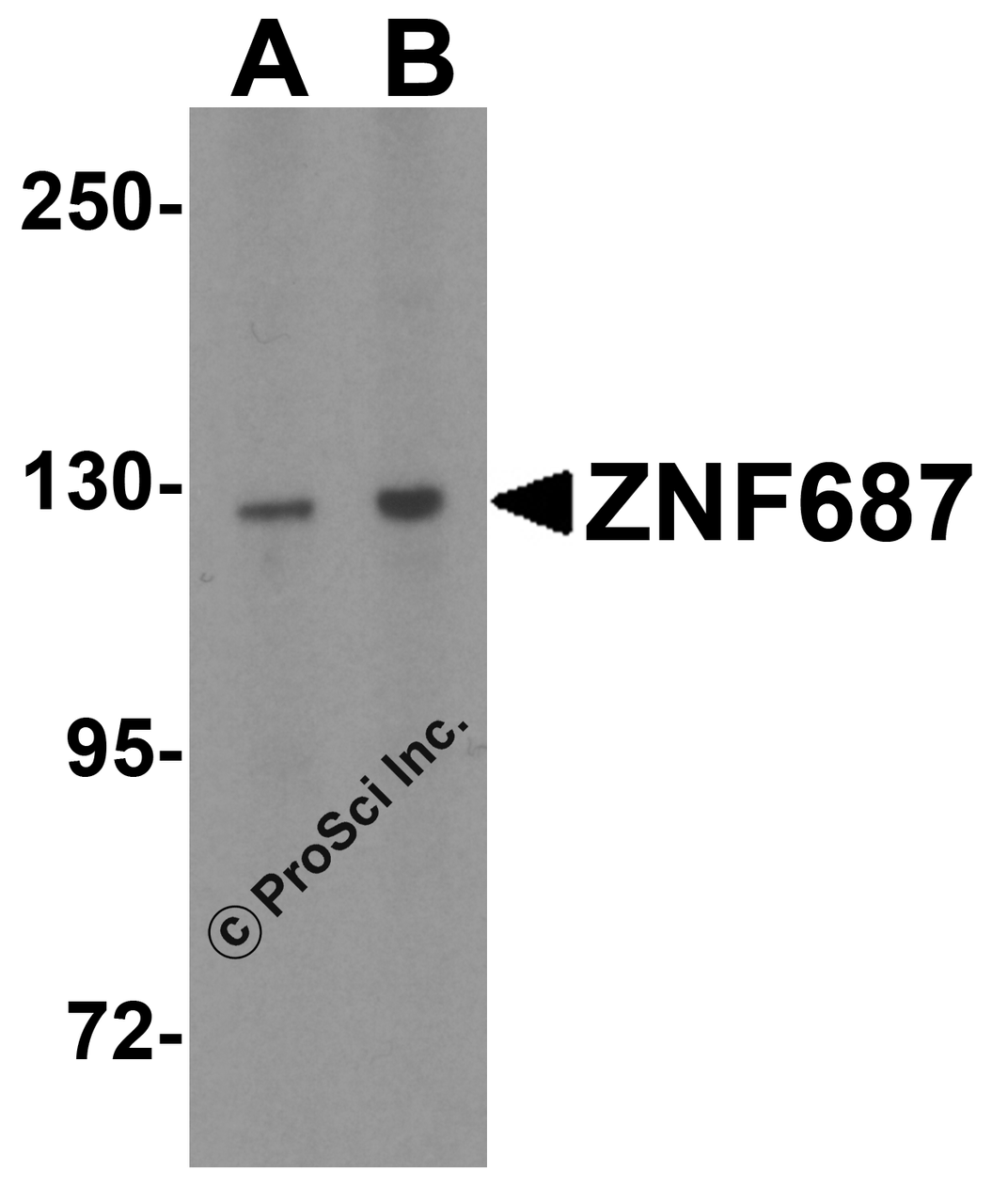
Application: ZNF687 antibody can be used for detection of ZNF687 by Western blot at 0.5 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples and Immunofluorescence in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: ZNF687 antibody is human specific. At least three isoforms of ZNF687 are known to exist; this antibody will only detect the largest isoform.
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1201 - HeLa Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: Cat. No. 17-005 - Jurkat Cell Slide
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Predicted: 125 kDa
Observed: 129 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: ZNF687 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: ZNF687 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: ZNF687 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: ZNF687 Antibody: KIAA1441, Zinc finger protein 687
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: ZNF687 Antibody: The zinc finger protein 687 (ZNF687) was initially identified as a translocation partner gene with RUNX1 in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) . Little is known of the function of the ZNF687 protein, but it has been shown to weakly interact with the Ring1/Rnf2 RING finger protein member of the Polycomb group of proteins, suggesting it may be involved in the chromatin-modifying complexes essential for embryonic development and stem cell renewal. Other evidence suggests that ZNF687 may be part of a transcriptional network that also includes ZNF592 and ZMYMD8.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL