Product Description
MFSD1 Antibody | 6023 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Bovine: (100%) , Chicken: (78%)
Immunogen: MFSD1 antibody was raised against an 18 amino acid synthetic peptide near the center of human MFSD1.
The immunogen is located within amino acids 220 - 270 of MFSD1.
Research Area: Homeostasis
Tested Application: E, WB, IHC-P
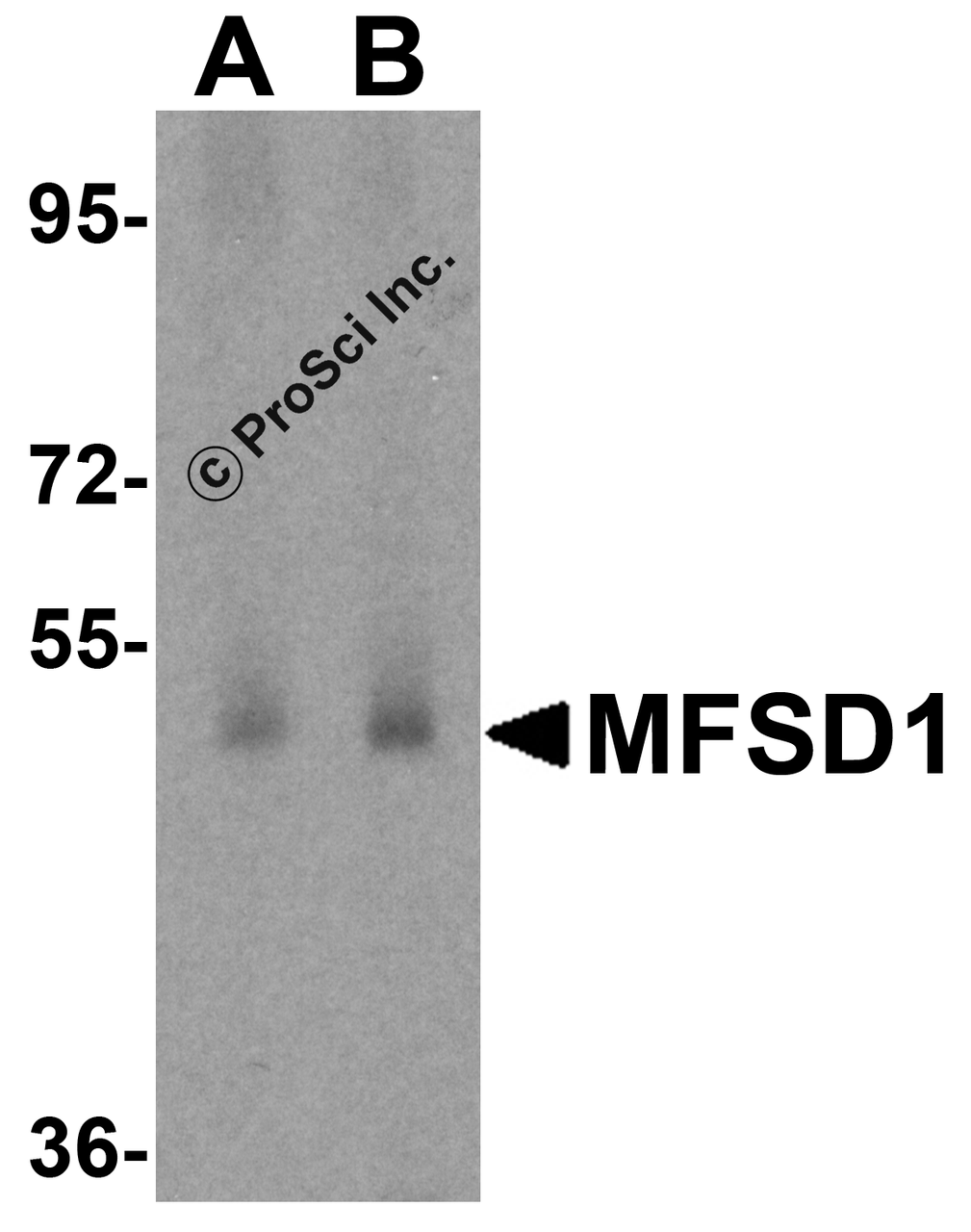
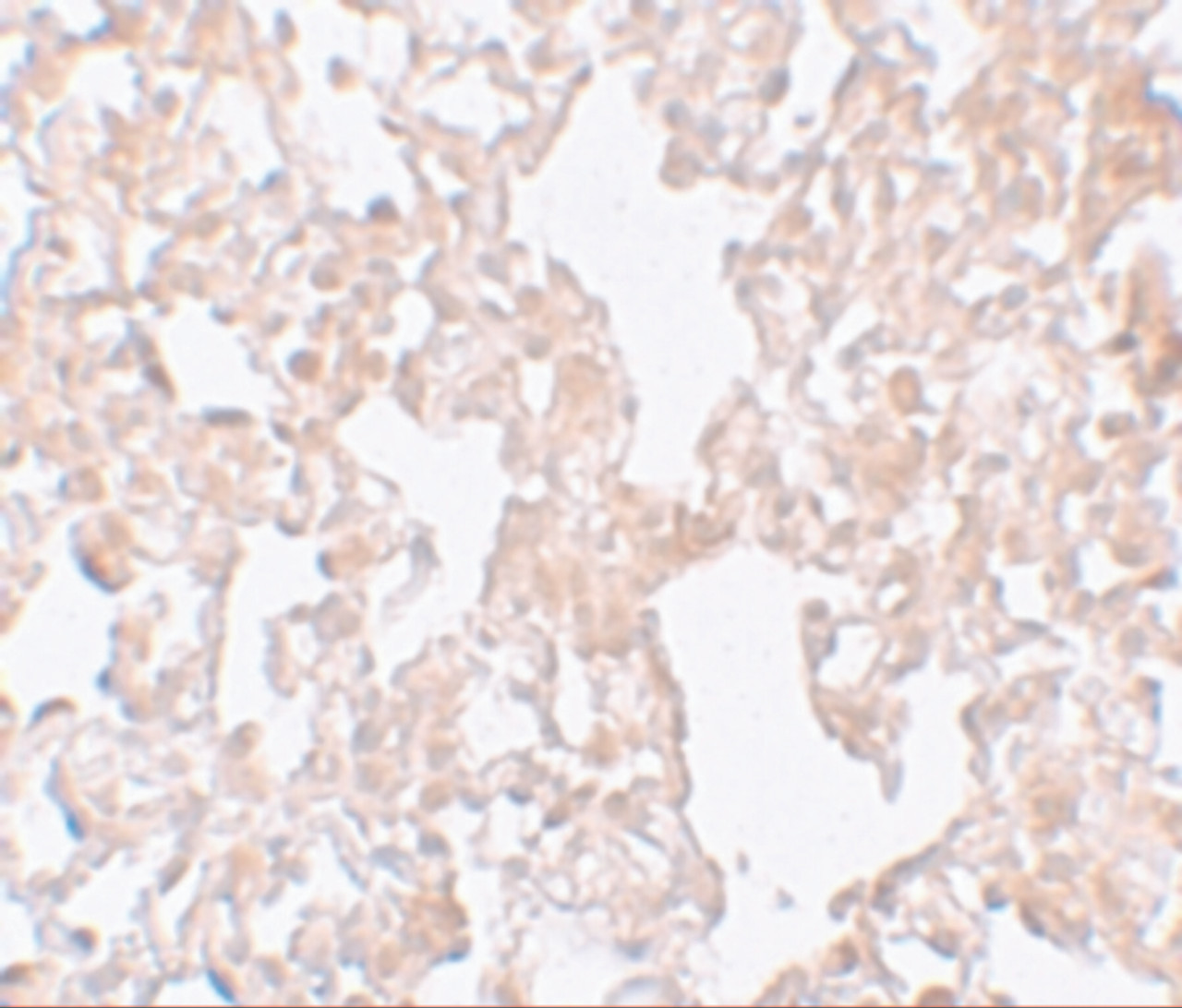
Application: MFSD1 antibody can be used for detection of MFSD1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 10 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples and Immunohistochemistry in rat samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1313 - Human Testis Tissue Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: MFSD1 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: MFSD1 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: MFSD1 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: MFSD1 Antibody: SMAP4, SMAP4, UG0581B09, Major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 1, Smooth muscle cell-associated protein 4, SMAP-4
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: MFSD1 Antibody: Multidrug transporters, such as MFSD1, are membrane proteins that expel a wide spectrum of cytotoxic compounds from the cell and render cells resistant to multiple drugs. The Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) is a large and diverse group of secondary transporters that include uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. Members of this family are found in all living organisms and are highly represented in bacteria. MFS members are capable of transporting various substrates such as sugars, polyols, drugs, neurotransmitters, amino acids, peptides, and inorganic anions, although most members are substrate-specific. MFS have provided important insight into the mechanism underlying multidrug transport. MFSD1 is still poorly understood.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL