Product Description
VKORC1 Antibody | 6795 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Bovine: (100%) , Rat: (87%)
Immunogen: VKORC1 antibody was raised against a 15 amino acid synthetic peptide near the amino terminus of human VKORC1.
The immunogen is located within the first 50 amino acids of VKORC1.
Research Area: Homeostasis
Tested Application: E, WB, IHC-P, IF
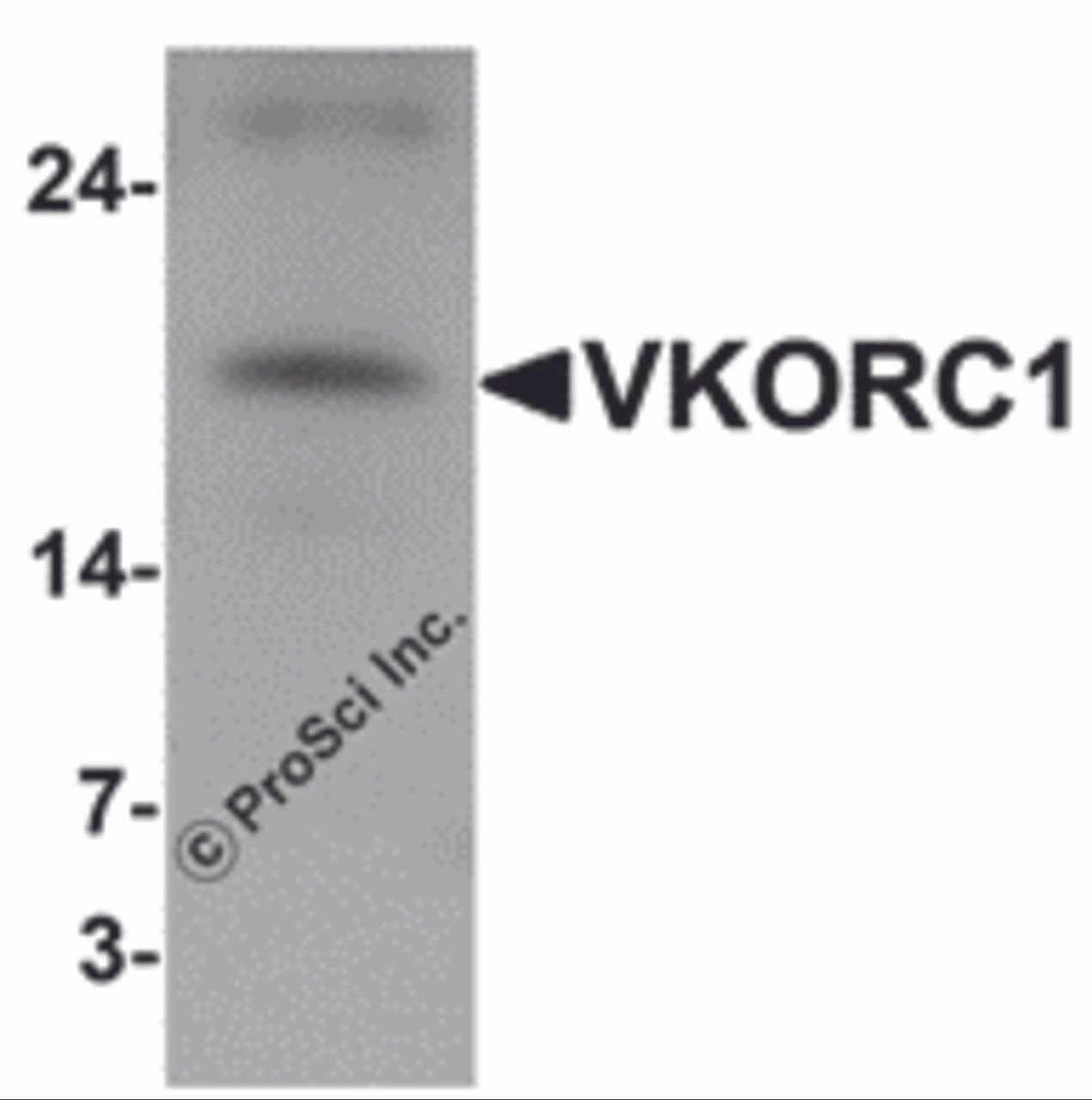
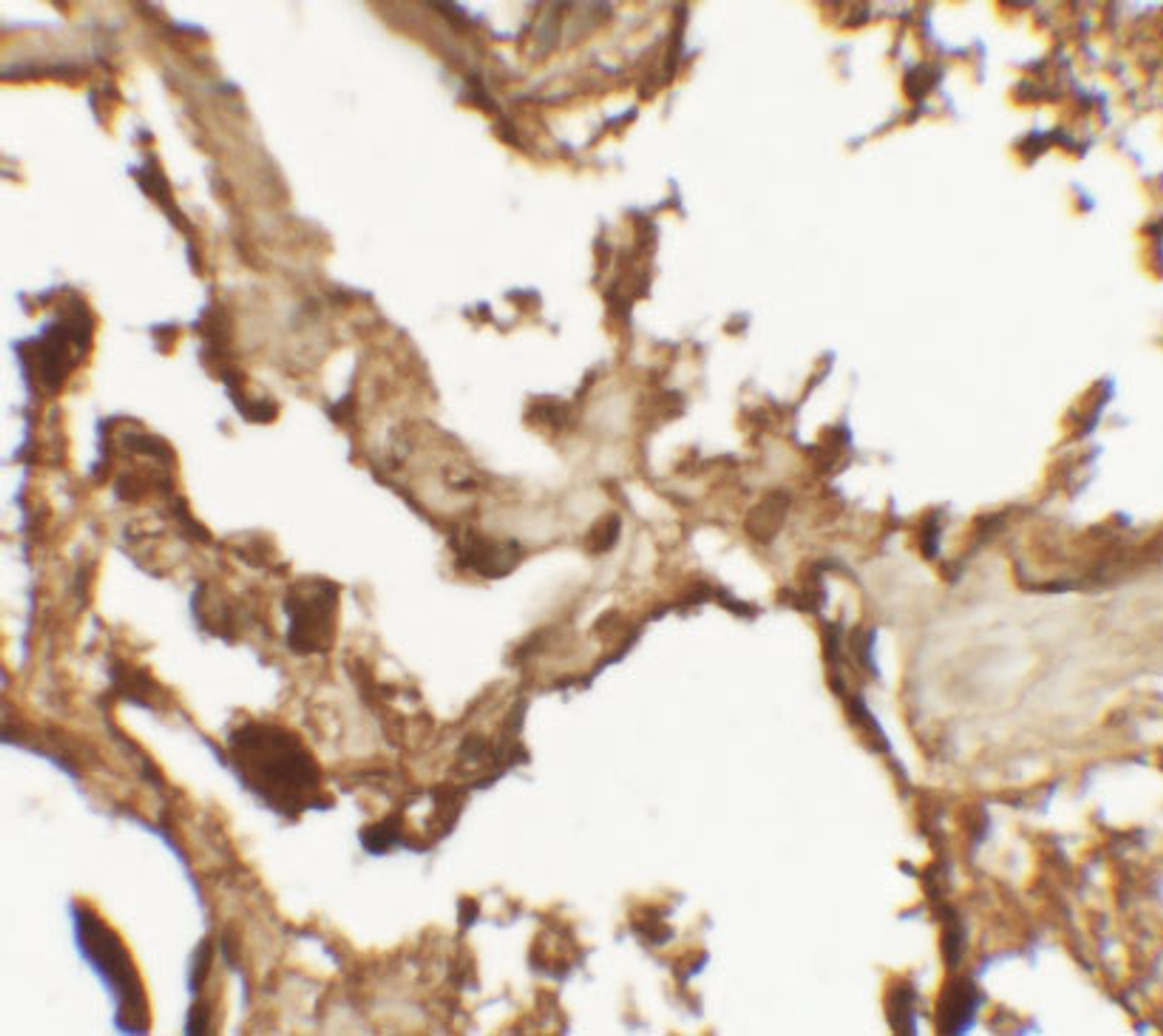
Application: VKORC1 antibody can be used for detection of VKORC1 by Western blot at 1 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2.5 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 5 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples; Immunohistochemistry in human samples and Immunofluorescence in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1203 - A549 Cell Lysate
Positive Control 2: Cat. No. 10-101 - Human Lung Tissue Slide
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: VKORC1 Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: VKORC1 Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: VKORC1 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Alternate Name: VKORC1 Antibody: VKOR, MST134, MST576, VKCFD2, EDTP308, IMAGE3455200, VKOR, MSTP134, MSTP576, UNQ308/PRO351, Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1, Vitamin K1 2, 3-epoxide reductase subunit 1
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: VKORC1 Antibody: Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (VKORC1) is the enzyme that is responsible for reducing vitamin K 2, 3-epoxide to the enzymatically activated form which is essential for blood clotting. This enzymatically activated form of vitamin K is a reduced form required for the carboxylation of glutamic acid residues in some blood-clotting proteins. Fatal bleeding can be caused by vitamin K deficiency and by the vitamin K antagonist warfarin, and it is VKORC1 that is sensitive to warfarin. In humans, mutations in this gene can be associated with deficiencies in vitamin-K-dependent clotting factors and, in humans and rats, with warfarin resistance.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL