Product Description
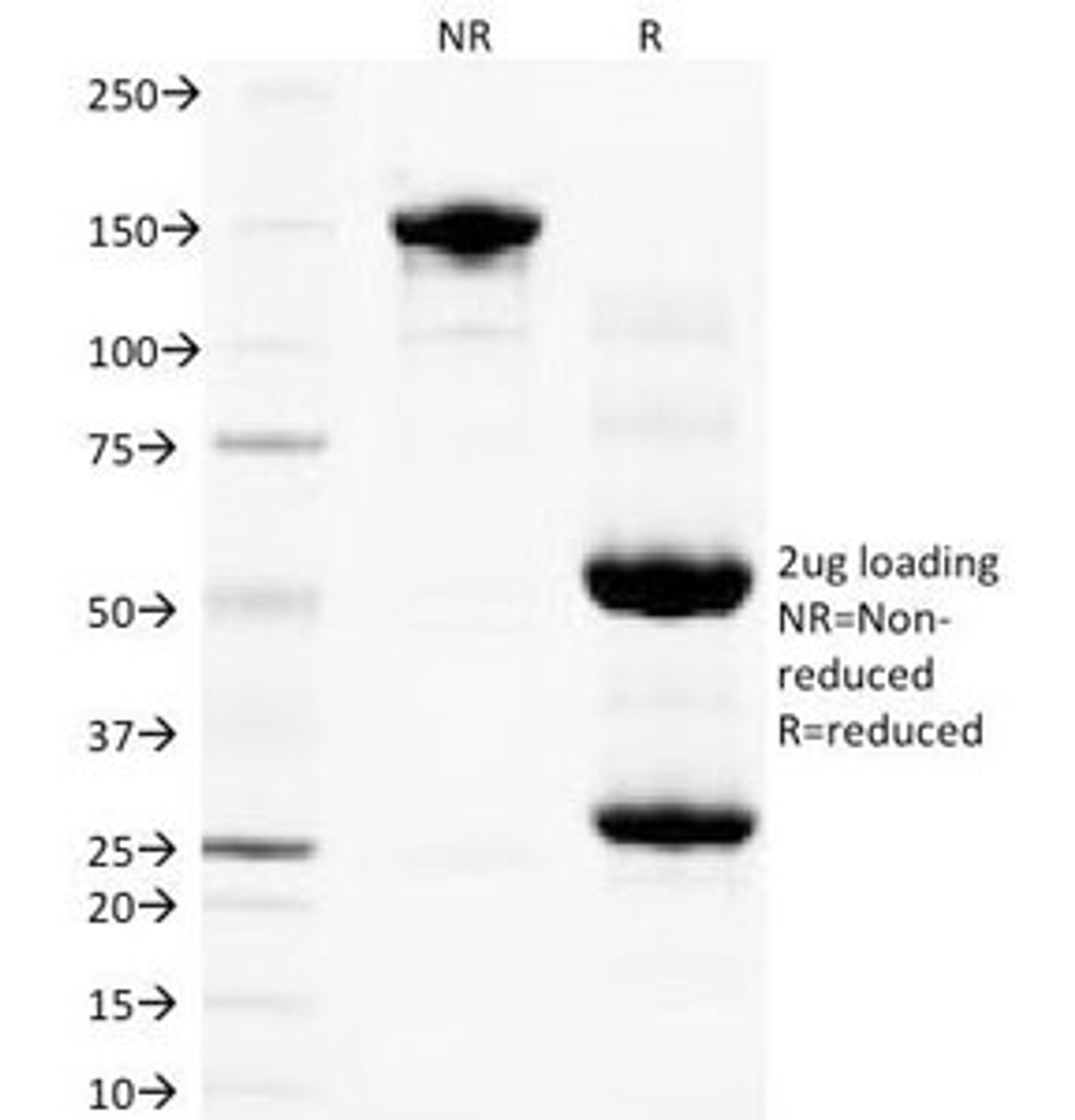
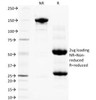
PLGF Antibody [PLGF94] | 33-187 | ProSci
Host: Mouse
Reactivity: Human
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Recombinant human protein was used as the immunogen for this PLGF antibody.
Research Area: Cancer, Obesity, Signal Transduction
Tested Application: WB, E, Func
Application: ELISA: order BSA/azide-free format
Functional testing: order BSA/azide free format
The concentration stated for each application is a general starting point. Variations in protocols, secondaries and substrates may require the PLGF antibody to be titered up or down for optimal performance.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Protein G purified PLGF antibody
Clonality: Monoclonal
Clone: PLGF94
Isotype: IgG1, kappa
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.1 mg/ml BSA and 0.05% sodium azide
Concentration: 0.2 mg/mL
Storage Condition: Aliquot and Store at 2-8˚C. Avoid freez-thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: Placenta growth factor, PlGF, PGF, PGFL, PLGF
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher
BACKGROUND: The onset of angiogenesis is believed to be an early event in tumorigenesis and may facilitate tumor progression and metastasis. Several growth factors with angiogenic activity have been described. These include fibroblast-, platelet derived-, vascular endothelial- and placenta- growth factor (PLGF) . Like vascular endothelial growth factor, several PLGF variants have been shown to arise from alternative mRNA splicings. Evidence has suggested VEGF to be an obligatory component in PLGF signaling. While VEGF homodimers and VEGF/PLGF heterodimers function as potent mediators of mitogenic and chemotactic responses in endothelial cells, PLGF homodimers are effectual only at extremely high concentrations. Indeed, many of the physiological effects attributed to VEGF may actually be a result of VEGF/PLGF. VEGF and PLGF share a common receptor, Flt-1, and may also activate Flk-1/KDR.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL

![PLGF Antibody [PLGF94] PLGF Antibody [PLGF94]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/1280x1280/products/575050/811262/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__54997.1649091798.png?c=2)
![PLGF Antibody [PLGF94] PLGF Antibody [PLGF94]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/100x100/products/575050/811262/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__54997.1649091798.png?c=2)
![PLGF Antibody [PLGF94] PLGF Antibody [PLGF94]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/575050/811262/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__54997.1649091798.png?c=2)




