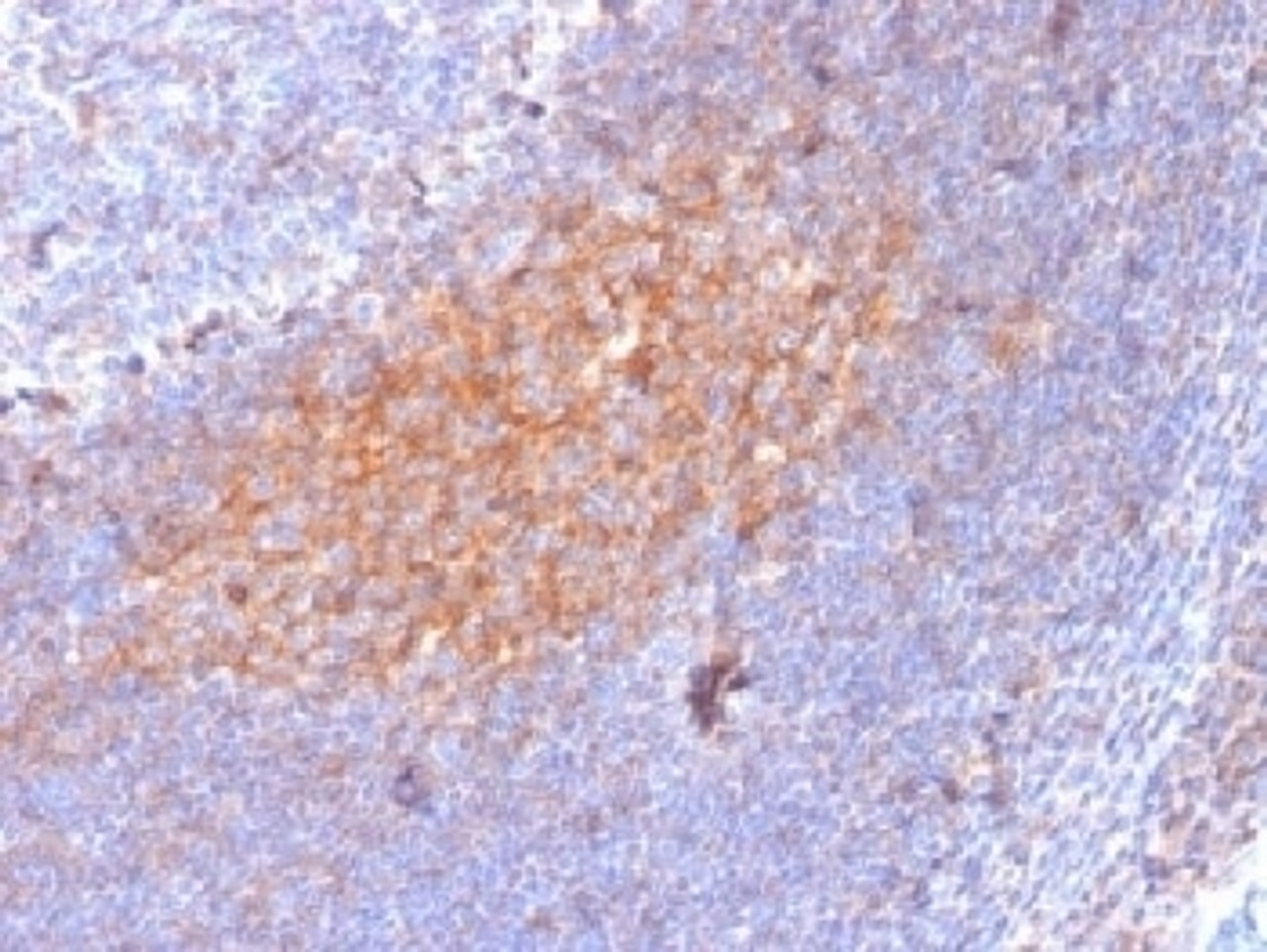
Product Description
CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22] | 33-829 | ProSci
Host: Mouse
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: A B-cell line derived from a Burkitt lymphoma was used as the immunogen for the CD81 antibody.
Research Area: Infectious Disease
Tested Application: Flow, IF, WB, IHC-P, Func
Application: Flow Cytometry: 0.5-1 ug/million cells in 0.1ml
Immunofluorescence: 0.5-1 ug/ml
WB: 0.5-1 ug/ml
Functional Studies: order BSA free formulation
IHC (FFPE) : 0.5-1 ug/ml for 30 min at RT
Optimal dilution of the CD81 antibody should be determined by the researcher.
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: N/A
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: N/A
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Protein G affinity chromatography
Clonality: Monoclonal
Clone: 1.3.3.22
Isotype: IgG1, kappa
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.1 mg/ml BSA and 0.05% sodium azide
Concentration: 0.2 mg/mL
Storage Condition: Aliquot and Store at 2-8˚C. Avoid freez-thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: CD81 Antibody: S5.7, CVID6, TAPA1, TSPAN28, CD81 antigen, 26 kDa cell surface protein TAPA-1, Tspan-28
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher
BACKGROUND: This mAb recognizes a protein of 26kDa, identified as CD81 (Workshop VI; Code CD81.1) . CD81 has a very broad cellular distribution, being expressed on T- and B-lymphocytes, NK cells, thymocytes, eosinophils, fibroblasts, epithelial and endothelial cells. Neutrophils, erythrocytes and platelets are negative, while monocytes are variably positive. CD81 is a member of a family of tetraspans transmembrane proteins, including CD9, CD37, CD53, CD63, and CD82. It associates with CD19, CD21, Leu 13, and integrins on cell membrane and is involved in signal transduction in B lymphocyte development and cell adhesion. CD81 also acts as a receptor for the envelope protein E2 of chronic hepatitis C virus. Antibodies to CD81 have anti-proliferative effects on different lymphoid cell lines, particularly those derived from large cell lymphomas.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL

![CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22] CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/1280x1280/products/575623/812615/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__36231.1649091985.png?c=2)

![CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22] CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/100x100/products/575623/812615/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__36231.1649091985.png?c=2)

![CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22] CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/575623/812615/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__36231.1649091985.png?c=2)
![CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22], Rabbit IgG CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22], Rabbit IgG](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/823997/1115581/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__16731.1649084691__20868.1649235586__20251.1649248189__62442.1657533733.png?c=2)
![CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22], Mouse IgG1 CD81 Antibody [1.3.3.22], Mouse IgG1](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/823996/1115580/porsci_lo__79508.1648973713__16731.1649084691__20868.1649235586__20251.1649248189__42221.1657533733.png?c=2)


![APC Anti-Human CD81 Antibody[1.3.3.22] | E-AB-F1073E APC Anti-Human CD81 Antibody[1.3.3.22] | E-AB-F1073E](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/439280/642127/elabscience__13538.1643193164__44410.1643194172__74326.1647355450.png?c=2)