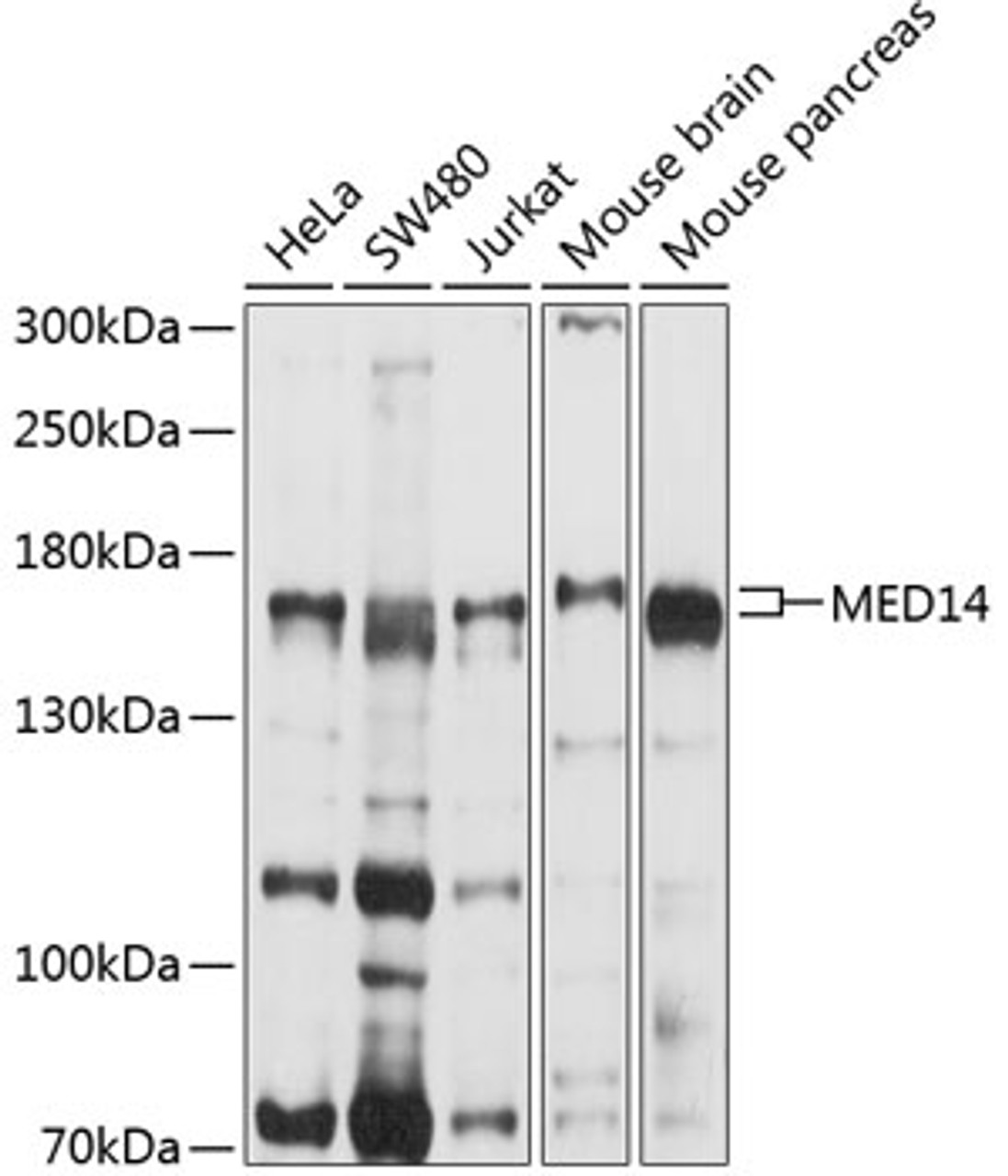
Product Description
MED14 Antibody | 13-661 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: N/A
Immunogen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 470-650 of human MED14 (NP_004220.2) .
Research Area: Other
Tested Application: WB
Application: WB: 1:500 - 1:2000
Specificiy: N/A
Positive Control 1: HeLa
Positive Control 2: SW480
Positive Control 3: Jurkat
Positive Control 4: Mouse brain
Positive Control 5: Mouse pancreas
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Observed: 150kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: Affinity purification
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Concentration: N/A
Storage Condition: Store at -20˚C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Alternate Name: Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 14, Activator-recruited cofactor 150 kDa component, ARC150, Cofactor required for Sp1 transcriptional activation subunit 2, CRSP complex subunit 2, Mediator complex subunit 14, RGR1 homolog, hRGR1, Thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex 170 kDa component, Trap170, Transcriptional coactivator CRSP150, Vitamin D3 receptor-interacting protein complex 150 kDa component, DRIP150, MED14
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: The activation of gene transcription is a multistep process that is triggered by factors that recognize transcriptional enhancer sites in DNA. These factors work with co-activators to direct transcriptional initiation by the RNA polymerase II apparatus. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the CRSP (cofactor required for SP1 activation) complex, which, along with TFIID, is required for efficient activation by SP1. This protein is also a component of other multisubunit complexes e.g. thyroid hormone receptor- (TR-) associated proteins which interact with TR and facilitate TR function on DNA templates in conjunction with initiation factors and cofactors. This protein contains a bipartite nuclear localization signal. This gene is known to escape chromosome X-inactivation.
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL