Product Description
HDAC1 Antibody | 7897 | ProSci
Host: Rabbit
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Homology: Predicted species reactivity based on immunogen sequence: Bovine: (100%)
Immunogen: HDAC1 antibody was raised against a 19 amino acid peptide near the carboxy terminus of human HDAC1.
The immunogen is located within the last 50 amino acids of HDAC1.
Research Area: Cell Cycle, Stem Cell
Tested Application: E, WB
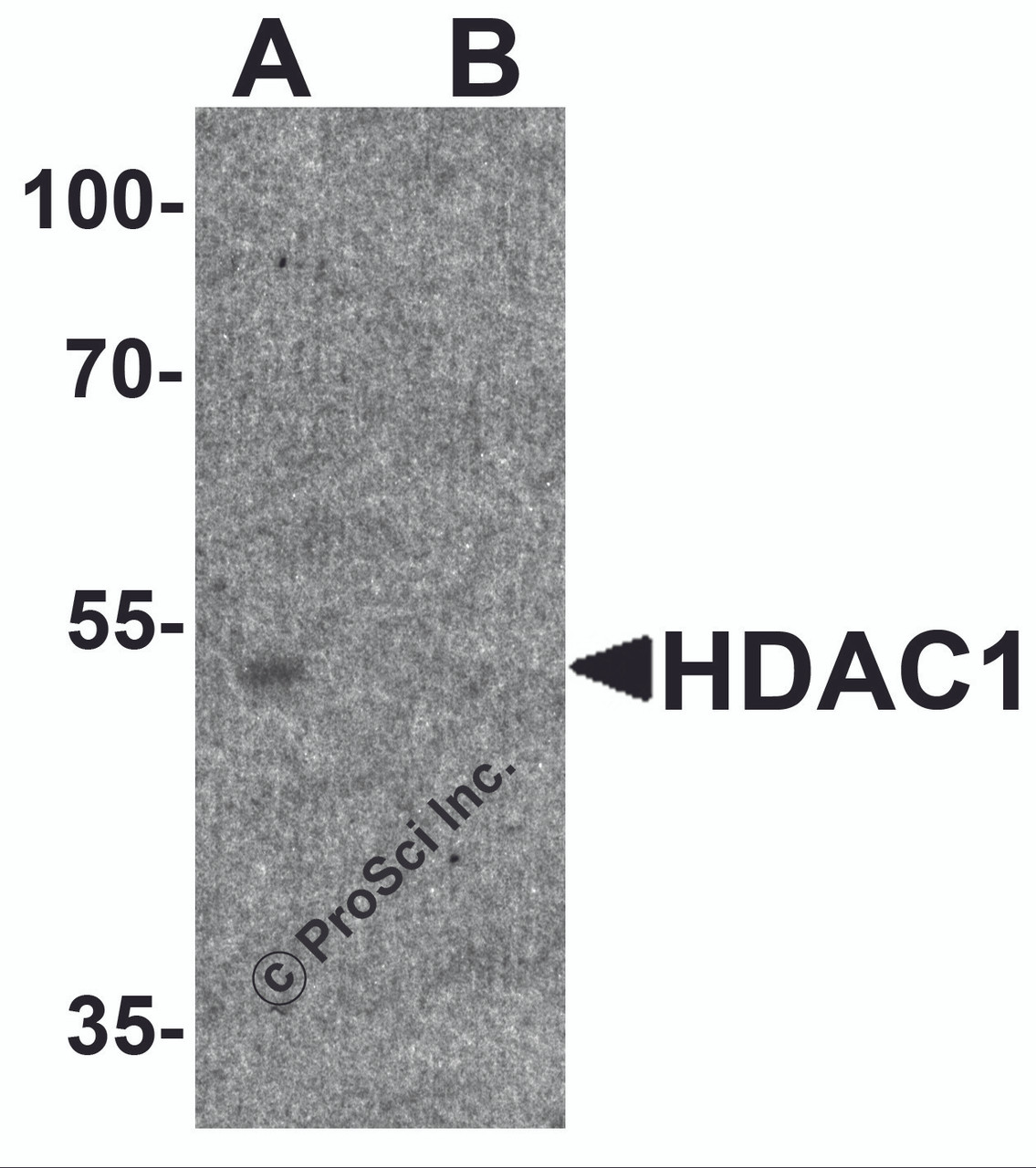
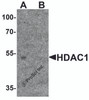
Application: HDAC1 antibody can be used for detection of HDAC1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 μg/ml.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Specificiy: HDAC1 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. HDAC1 antibody is predicted to not cross-react with other members of the HDAC family.
Positive Control 1: Cat. No. 1303 - Human Brain Tissue Lysate
Positive Control 2: N/A
Positive Control 3: N/A
Positive Control 4: N/A
Positive Control 5: N/A
Positive Control 6: N/A
Molecular Weight: Predicted: 53 kDa
Observed: 54 kDa
Validation: N/A
Isoform: N/A
Purification: HDAC1 antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Clonality: Polyclonal
Clone: N/A
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Unconjugated
Physical State: Liquid
Buffer: HDAC1 antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration: 1 mg/mL
Storage Condition: HDAC1 antibody can be stored at 4˚C for three months and -20˚C, stable for up to one year.
Alternate Name: HDAC1 Antibody: HD1, RPD3, GON-10, RPD3L1, Histone deacetylase 1, HD1
User Note: Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
BACKGROUND: The histone deacetylase (HDAC) family contains multiple members which are divided into four classes. Class I of the HDAC family comprises four members, HDAC1, 2, 3, and 8, each of which contains a deacetylase domain and exhibits a different, individual substrate specificity and function in vivo (1) . HDAC1 is responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) (1, 2) . HDAC1 gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events (3, 4) .
 Euro
Euro
 USD
USD
 British Pound
British Pound
 NULL
NULL





![HDAC1 Antibody [AMM02460G] HDAC1 Antibody [AMM02460G]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-452hpg8iuh/images/stencil/500x659/products/869136/1161203/logo__92149.1659788186__45727.1659865397.png?c=2)






